
Incorrect answer for Image Quiz: Dermatology-A dog with a suddenly crusty, itchy muzzle

Incorrect answer for Image Quiz: Dermatology-A dog with a suddenly crusty, itchy muzzle
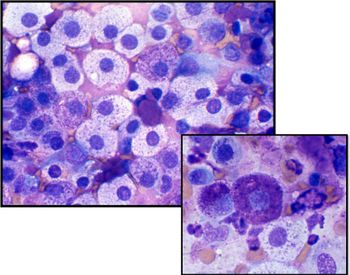
Correct answer for Image Quiz: Cytology-A subcutaneous mass in a senior dog

Dr. Joseph Bartges discusses how a new set of guidelines provide an important framework.

These guidelines may help counteract the rise in antibacterial resistance as well as lessen the overall impact of misuse on patient health.

From the 2011 ACVIM Forum: Does extralabel use of this drug promote urolith formation in dogs?
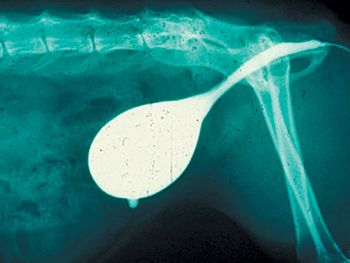
During the past two decades, clinical research has improved our abiilty to detect several types of lower urinary tract disease in male and female cats.

This study examined the effect of an exogenous glycosaminoglycan on cats with this painful urinary condition.
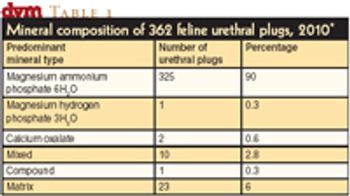
A look at composition provides insight into ways to prevent plugs in the first place.

Persistent proteinuria of renal origin is an important marker of chronic kidney disease (CKD) in dogs and cats. Unfortunately, due to the high incidence of false-positive results for proteinuria on the urine dipstick screening test and proteinuria associated with lower urinary tract inflammation, positive reactions for urine protein are quite common and therefore often disregarded.

Over the last several years, there has been a shift in the mineral content of uroliths in cats from predominantly magnesium-ammonium phosphate (MAP) to calcium oxalate (CaOx). Of the nephroliths and ureteroliths analyzed by the Minnesota Urolith Center in 2002, 70% of 170 renolith submissions and 98% of ureterolith submissions were CaOx.

By altering pre-glomerular resistance, healthy kidneys can maintain relatively stable glomerular capillary pressures despite variations in systemic blood pressure. This process is termed "renal autoregulation". Autoregulation can be reduced when renal disease results in loss of nephrons.

In spite of repeated efforts, pleas for Divine intervention, and promises to God, you cannot get the catheter to pass into the bladder

Azotemia is defined as increased concentrations of urea and creatinine (and other nonproteinaceous nitrogenous substances) in the blood. The interpretation of serum urea nitrogen and creatinine concentrations as a measure of renal function requires a knowledge of the production and excretion of these substances.

Most bacterial infections of the lower urinary tract respond quickly to antimicrobial treatment; however, urinary tract infections (UTI) associated with defects in the host immune system (complicated UTI) often fail to respond or recur after antibiotic withdrawal and can be a therapeutic challenge.

Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a common problem that affects an estimated 0.5 to 7% of dogs. Radiographic signs of osteoarthritis (OA) occur in 20% of dogs.

Hyperthyroidism is one of the most commonly diagnosed diseases of the older cat. Geriatric cats with hyperthyroidism may also have concurrent chronic kidney disease (CKD). Systemic hypertension, proteinuria, and urinary tract infection (UTI) can be consequences of either hyperthyroidism or CKD.

Feline lower urinary tract diseases are characterized by hematuria, pollakiuria, and dysuria, and are common problems encountered in feline practice. It is estimated that they affect over one half million cats in the United States annually. Although there are numerous recognized causes of these signs, the exact cause is never identified in the majority of cases.

Anticipate and treat these seven conditions that can result from urethral obstruction.

What is the risk of leaving calculi after cystotomy?

In a recent study, researchers evaluated the use of indwelling, double-pigtail ureteral stents in dogs with ureteral obstruction secondary to trigonal malignancy.

Dr. Matthew Beal discusses this promising noninvasive alternative to cystostomy tubes.

Watch our August 2011 issue for results of the survey.


What is the most effective treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia?

Don't fall prey to 6 oft-repeated urinalysis myths.