Be sure to look a little deeper when using this technique during your search for a ruptured bladder to prevent missing the diagnosis.

Be sure to look a little deeper when using this technique during your search for a ruptured bladder to prevent missing the diagnosis.

The goal of this study was to provide more recent data on the prevalence of acquired urinary incontinence.

An overview of diagnostic and treatment options for veterinary patients with signs of lower urinary tract disease.
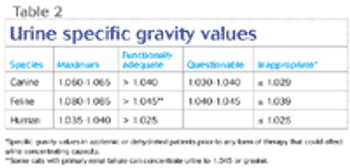
Several diagnostic factors must come into play when a veterinarian gets an abnormal result on this common test that investigates kidney function. (Part three of a four-part series.)

Work through this interactive case to help Olivia, a 2-year-old terrier mix, get over her urinary troubles.
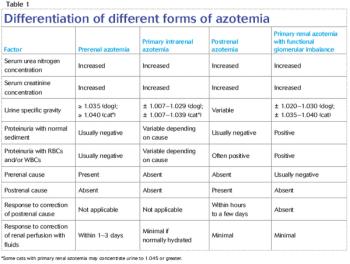
A look at the indications for this important part of a veterinary urinalysis and how to interpret the results. (Part two of a four-part series)

Visit these websites for veterinary behavior resources.

A look at whether this practice will thwart your results.

This idea will improve your urinalysis interpretation.

How would you interpret the results in these seven case presentations?

Past veterinary trends continue, but with therapeutic preventative options available, many plugs can be avoided.

Dr. Dawn Boothe discusses a good first-choice antimicrobial for empirical treatment of a urinary tract infection.
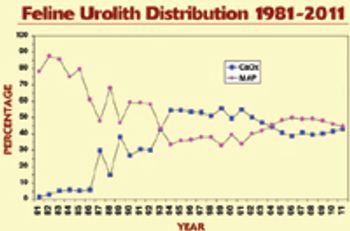
Dr. Carl Osborne tracks the trends of mineral composition in cats with urolithiasis.

St. Paul, Minn.-- Veterinarian Jody Lulich of the University of Minnesota was honored with the 2012 Mark L. Morris, Sr., Lifetime Achievement Award.

A recent study investigated this option for treating this common urinary tract malignancy.

Dr. Dawn Boothe discusses whether you should treat patients that have chronic bacteria in their urine yet no signs of infection.

This is a question in "BizQuiz: Is stationary or mobile equine veterinary practice right for you?"

This is a question in "BizQuiz: Is stationary or mobile equine veterinary practice right for you?"


This is a question in "BizQuiz: Is stationary or mobile equine veterinary practice right for you?"

This is a question in "BizQuiz: Is stationary or mobile equine veterinary practice right for you?"

Image Quiz: Dermatology-The case of the blind Akita

Look outside the urinary tract-as well as in the cat's environment-for diagnostic and therapeutic answers.

See how one cat diagnosed with this syndrome was successfully treated.

The causes of urinary incontinence classically are divided into neurogenic or non-neurogenic categories.