
Insulin has become increasingly important in the treatment of dogs and cats with diabetes mellitus. Almost all dogs are classified with insulin-dependent or type 1 diabetes mellitus.

Insulin has become increasingly important in the treatment of dogs and cats with diabetes mellitus. Almost all dogs are classified with insulin-dependent or type 1 diabetes mellitus.

The pancreas has both endocrine and exocrine functions. The endocrine pancreas consists of the islets of Langerhans and is particularly important to carbohydrate metabolism.

Icterus is a term used to describe the clinical appearance of hyperbilirubinemia. While reference values may vary, in most instances a serum bilrubin > 1 mg/dl is considered abnormal but clinically detectable icterus usually does not occur until the bilirubin is > 3 mg/dl.

Dogs and cats frequently present for signs related to the urinary tract. These signs may be due to inappropriate urination (house soiling or urinary incontinence) or may relate to the act of voiding itself.

Nasal discharge is seen most commonly with diseases of the nasal passages, sinuses and nasopharynx. Occasionally disease involving the lower airways (trachea, bronchi, etc) can result in nasal discharge.

The fungal organisms most commonly associated with systemic disease are Blastomyces dermatitidis, Histoplasma capsulatum, Coccidioides immitis and cryptococcosis.

Endocrine emergencies are clinical presentations in which immediate recognition and treatment of the endocrine disorder is required to decrease patient morbidity and prevent mortality. Endocrine disorders that require this immediate recognition and treatment are adrenal insufficiency, pheochromocytoma, diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar diabetes mellitus, insulinoma, hypoparathyroidism, and myxedema coma in severe hypothyroidism.

Hyperthyroidism and chronic kidney disease are two common diseases of older cats. They may occur separately or in the same animal.

Inflammatory liver disease is second only to hepatic lipidosis as a cause of hepatobiliary disease in cats in the United States. Inflammatory liver diseases have been traditionally classified by their cellular infiltrate and pattern of distribution.

The liver plays an important role in carbohydrate, lipid and protein metabolism as well as vitamin and mineral storage. The liver is also vital in detoxification of metabolic products (ammonia, uric acid), hormones and drugs. There are several diseases of the liver in the dog that can result in inflammation. The two most common, acute and chronic hepatitis, will be the focus of this discussion.

The normal liver receives arterial blood from the hepatic artery and venous blood from the portal vein. Regarding arterial blood flow, the celiac artery branches off of the aorta and the hepatic artery branches off of the celiac artery.

Thyroid hormones influence many body systems. Thyroid hormones are involved in the development of the nervous and musculoskeletal systems. Thyroid hormones are also important to normal cardiorespiratory function, other hormones and enzyme systems, and red cell synthesis to name a few.

Insulin has become increasingly important in the treatment of dogs and cats with diabetes mellitus. Almost all dogs are classified with insulin-dependent or type 1 diabetes mellitus. Although up to 60% of cats are non insulin-dependent or type 2 diabetics at the time of diagnosis1, early intervention with exogenous insulin is an important component to achieving remission and preserving the function of insulin-secreting beta cells.

The adrenal gland consists of two distinct regions, the outer cortex and inner medulla. The cortex consists of three distinct layers that produce mineralocorticoids (aldosterone), glucocorticoids and androgens. Collectively these hormones are sometimes referred to as corticosteroids. The medulla produces catecholamines including epinephrine, norepinephrine and dopamine.
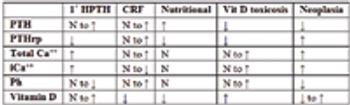
Calcium is involved in many cellular and extracellular processes that include neuromuscular transmission, muscle contraction/tone, hormone secretion, bone homeostasis, coagulation, membrane transport systems, and other cell regulatory pathways. Calcium is measured as ionized (active form, roughly 50%) or total (ionized + albumin bound + anion bound).

The adrenal gland consists of two distinct regions, the outer cortex and inner medulla. The cortex consists of three distinct layers that produce mineralocorticoids (aldosterone), glucocorticoids and androgens.

Inflammatory liver disease is second only to hepatic lipidosis as a cause of hepatobiliary disease in cats in the United States. Inflammatory liver diseases have been traditionally classified by their cellular infiltrate and pattern of distribution.

Insulin has become increasingly important in the treatment of dogs and cats with diabetes mellitus. Almost all dogs are classified with insulin-dependent or type 1 diabetes mellitus.

The normal liver receives arterial blood from the hepatic artery and venous blood from the portal vein. Regarding arterial blood flow, the celiac artery branches off of the aorta and the hepatic artery branches off of the celiac artery.

The liver plays an important role in carbohydrate, lipid and protein metabolism as well as vitamin and mineral storage. The liver is also vital in detoxification of metabolic products (ammonia, uric acid), hormones and drugs.

The hypothalamus secretes thyrotropin-releasing hormone in response to nervous stimuli. The TRH then stimulates the pituitary gland to secrete thyrotropin-secreting hormone (TSH).

In the United States there is limited experience with hypophysectomy for pituitary tumors but outside the United States this surgery has been performed with good results.

The classification of diabetes mellitus has changed over the years in both human and veterinary patients.

Insulin has become increasingly important in the treatment of dogs and cats with diabetes mellitus.

This is a common endocrinopathy of the cat. The disease is most common in older cats but occasionally occurs in younger cats.

Hyperadrenocorticism (HAC) is a common endocrine disease of the dog.

Hypoadrenocorticism occurs as a result of a deficiency in glucocorticoids and, in most cases, mineralocorticoids.

Mineralocorticoids are hormones produced by the adrenal glands that regulate fluid and electrolyte balance.

Dogs typically develop insulin dependent, or type I, diabetes mellitus.

Insulin was first discovered in 1921 by Frederick Banting and colleagues.

Published: November 1st 2010 | Updated:

Published: November 1st 2010 | Updated:

Published: November 1st 2010 | Updated:

Published: November 1st 2010 | Updated:

Published: November 1st 2010 | Updated:

Published: November 1st 2010 | Updated: