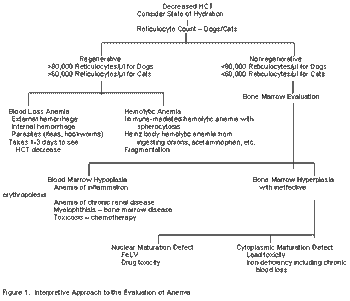
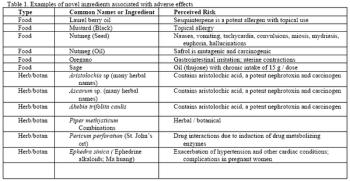
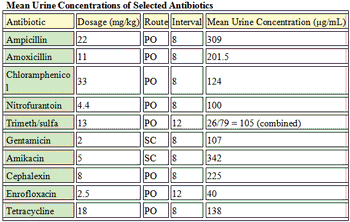
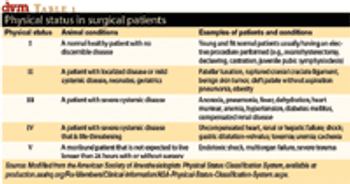
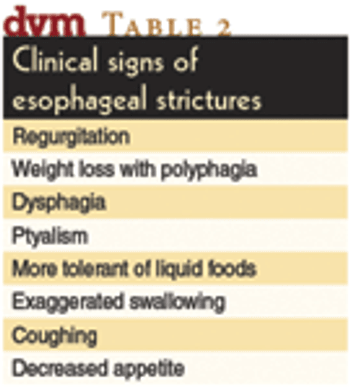
One can usually find many sources of information about drugs: FDA website, drug company websites and technical reports, VIN, journals, trade magazines, and so on. The important skill required of veterinarians is to assess that information to determine its usefulness in your daily practice. Below are some principles of evaluating drug information, with the goal of improving treatment and the practice of medicine.