Todd R. Tams, DVM, DACVIM
Articles by Todd R. Tams, DVM, DACVIM

It is important that the clinician formulate a treatment protocol based on a correlation of clinical course, laboratory and gross findings, and histologic findings rather than relying on histologic changes alone. Although treatment principles for cats and dogs with IBD are similar, drug selection and dosage regimens vary between these two species in some situations.

Antibiotic therapy is indicated for treatment of suppurative hepatitis, cholangiohepatitis and hepatic encephalopathy, and prevention of septicemia. The bactericidal function of the hepatic reticuloendothelial (RE) system may be compromised in hepatic disease, especially if hepatic blood flow or oxygen tension is altered, resulting in septicemia.

Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) currently is recognized as a common and important medical problem in cats. Three general types of clinical presentations have been identified in cats with idiopathic IBD: (1) a clinical course characterized primarily by vomiting, (2) a clinical course characterized primarily by diarrhea, and (3) a clinical course that includes both vomiting and diarrhea as primary signs. Associated clinical signs can include change in appetite (anorexia, inappetence, or ravenousness), weight loss, and lethargy. In some cats, the clinical signs are cyclic; they seem to flare up and then abate in a predictable pattern.

Disease caused by parvovirus in dogs (destruction of intestinal crypt epithelium, lymphocyte depletion, neutropenia) is generally more severe than that caused by coronavirus (destruction of intestinal villi). Coronavirus enteritis is often characterized by mild and self-limiting clinical signs.

Initial nonspecific management of vomiting includes NPO (in minor cases a 6-12 hour period of nothing per os may be all that is required), fluid support, and antiemetics. Initial feeding includes small portions of a low fat, single source protein diet starting 6-12 hours after vomiting has ceased.

Vomiting is among the most common reasons that dogs and cats are presented for evaluation. Because there are a multitude of causes of vomiting, ranging from simple to complex, this can be a challenging problem for clinicians to accurately diagnose and manage.

Giardia, Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin, and Cryptosporidium are important causes of diarrhea in dogs and cats. Tritrichomonas foetus is an important problem in cats. These disorders should be investigated early in the course of diarrhea, whether it is persistent or intermittent, along with evaluation for dietary causes of GI signs, nematode parasites, bacterial and viral causes, and acute idiopathic colitis.

Dysphagia is defined as difficult or painful swallowing. It may be due to obstruction, motility disturbance, or pain. Although dysphagia most commonly indicates a disorder involving the oral cavity or pharynx, esophageal disorders can cause this clinical sign as well.

The liver has more biochemical functions than any other organ of the body. It functions in hundreds of diverse metabolic activities including synthesis of plasma proteins; catabolism and storage of carbohydrates; synthesis, degradation, and storage of lipids; detoxification and excretion of many toxic agents; and the formation and elimination of bile.

Vomiting is among the most common reasons that dogs and cats are presented for evaluation. Because there are a multitude of causes of vomiting, ranging from simple to complex, this can be a challenging problem for clinicians to accurately diagnose and manage.

Dysphagia is defined as difficult or painful swallowing. It may be due to obstruction, motility disturbance, or pain. Although dysphagia most commonly indicates a disorder involving the oral cavity or pharynx, esophageal disorders can cause this clinical sign as well.

Giardia, Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin, and Cryptosporidium are important causes of diarrhea in dogs and cats. Tritrichomonas foetus is an important problem in cats. These disorders should be investigated early in the course of diarrhea, whether it is persistent or intermittent, along with evaluation for dietary causes of GI signs, nematode parasites, bacterial and viral causes, and acute idiopathic colitis.

Disease caused by parvovirus in dogs (destruction of intestinal crypt epithelium, lymphocyte depletion, neutropenia) is generally more severe than that caused by coronavirus (destruction of intestinal villi).

Vomiting is among the most common reasons that dogs and cats are presented for evaluation.

It is important that the clinician formulate a treatment protocol based on a correlation of clinical course, laboratory and gross findings, and histologic findings rather than relying on histologic changes alone.

Giardia, Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin, and Cryptosporidium are important causes of diarrhea in dogs and cats.

Initial nonspecific management of vomiting includes NPO (in minor cases a 6-12 hour period of nothing per os may be all that is required), fluid support, and antiemetics.
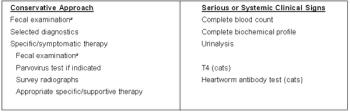
Vomiting is among the most common reasons that dogs and cats are presented for evaluation.

Initial nonspecific management of vomiting includes NPO (in minor cases a 6-12 hour period of nothing per os may be all that is required), fluid support, and antiemetics.

It is important that the clinician formulate a treatment protocol based on a correlation of clinical course, laboratory and gross findings, and histologic findings rather than relying on histologic changes alone.
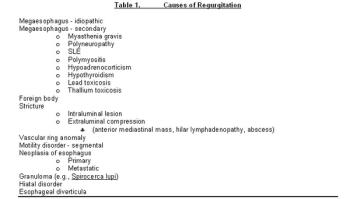
Dysphagia is defined as difficult or painful swallowing. It may be due to obstruction, motility disturbance, or pain.

Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) currently is recognized as a common and important medical problem in cats.

Giardia, Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin, and Cryptosporidium are important causes of diarrhea in dogs and cats.

Antibiotic therapy is indicated for treatment of suppurative hepatitis, cholangiohepatitis and hepatic encephalopathy, and prevention of septicemia.













