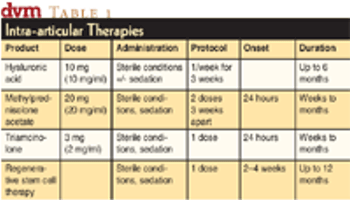
Check out these three options for optimal joint care and comfort.

Raleigh, N.C. -- A gene linked to a fatal neurodegenerative disease in American Staffordshire terriers was identified by veterinary researchers.


Corneal disease and damage resulting in cloudy, blue eyes has many causes.

Diet, supplements, drugs and cognitive and physical stimulation all play roles.

A Q&A with veterinary internist Barrak Pressler

Bacterial pneumonia is a common cause of disease in young foals.
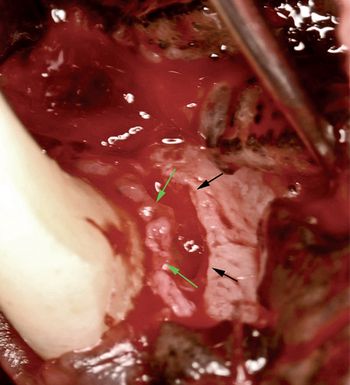
Weigh clinical, radiographic evidence as well as client expectations when approaching this preventable disease.
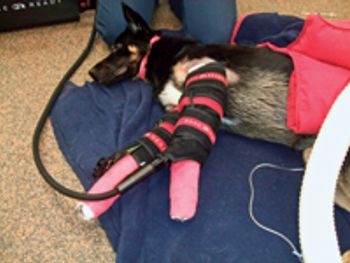
A variety of treatments can get patients back comfortably on all fours.

Bartonella species is a new and emerging bacterial pathogen for veterinarians.

Everything we have discussed to this point is actually about establishing a records plan that will allow us to serve the dairy industry of the future using the records that are efficiently gathered so we are not spending all of our time keeping or organizing the records. As our herds get larger, as the number of animals examined at any one time increases, as we are examining groups of diverse animals at one time, and as we struggle to maintain a cow side presence, the organization of the records becomes more critical.

The agricultural community is an extremely small percent of the general population and much of that population lives in densely populated areas of the country. They draw their perceptions of food animal care from their experiences and perceptions about zoos, their own companion animals, and the visual stories presented electronically from opponents of the animal industry.
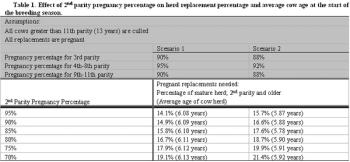
Because one goal of proper heifer development is to improve second parity pregnancy percentage, a beef producer may ask "what is the impact of higher pregnancy percentages during the second breeding season on costs and income?" Table 1 displays the effect of changing pregnancy percentage for first-calf heifers in 5-percentage point increments on the percent of the herd that must be replaced each year and the average age of the herd. In general, given the assumptions in the table, for every 5-percentage point improvement in first-calf heifer pregnancy percentage, the number of replacements needed for the herd decreases by about 1 percentage point and average cow age increases by .01 years.

The Food and Drug Administration Center for Veterinary Medicine (FDA CVM) approves drug labels. The Environmental Protection Agency approves pesticides and products used on premises.

Multiple physiologic mechanisms act in concert to maintain the concentration of ionized calcium in the extracellular fluid (ECF) within a very tightly-regulated range. Hypocalcemia most commonly occurs when the physiologic demand for calcium for fetal bone growth or milk production exceeds the dietary supply of calcium and overwhelms the homeostatic systems aimed at maintaining adequate ionized calcium in the ECF.

Lead-based paints, lead-based gasoline, solder, combustion residues, caulking compounds, improperly glazed pottery, batteries, buck-shots, sewage sludge, some canned commercial dog foods, electronic wastes, etc.

At the time of this writing, the focus on farm animals by the media (and likely therefore consumer perception) seems to be on antimicrobial use in animal agriculture and on farm animal welfare.

Suckling calves are commonly in contact with the breeding herd during early gestation, prior to the time the bovine fetus develops a competent immune system. As a result, PI suckling calves are considered to be the primary source of BVDV infection in breeding herds causing pregnancy loss, pre-weaning mortality and the induction of PI calves in the next generation.

The gastrointestinal tract is the primary route of exposure. Ethylene glycol is a small molecule (62 dalton) which undergoes rapid absorption from the gastrointestinal tract, distributes to the liver where it is rapidly metabolized by the hepatic alcohol dehydrogenase pathway to toxic metabolites (glycoaldehyde, glycolic acid, glyoxlic acid, oxalic acid, and formic acid), and is excreted in the urine. These metabolic intermediates (organic acids) induce severe metabolic acidosis, kidney failure and subsequent death, in exposed animals and humans.

In a 1996 survey of over 5,100 U.S. sheep producers, 9.4% of lambs born alive were reported to have died prior to weaning. Worldwide, hypothermia and starvation are considered to account for the majority of preweaning lamb losses, with predation and respiratory disease also being important causes.

"Susceptible" and "Resistant" are thrown around in the fields of microbiology, medicine, public health, and epidemiology with great frequency. Unfortunately, these classifications are often used in a manner inconsistent with their correct application.

This presentation attempts to summarize some of the major concerns in resistance development along with key articles explaining relevance, epidemiology, and prevalence. It is not intended to be an exhaustive review of the literature and the interested practitioner should use the cited literature herein as a basis for continued, extended reading.

The capacity to experience pain is considered to have a protective role by eliciting behavioral responses aimed at reducing further tissue damage and enhance wound healing. However, persistent pain syndromes offer no biological advantage and are associated with suffering and distress.
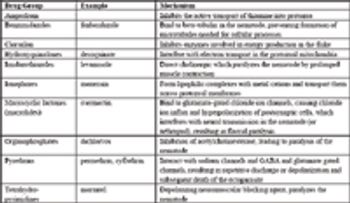
The science of how drugs work on the body (or the microorganism or parasite) is pharmacodymanics (its counterpart being pharmacokinetics, how the body works on the drug). In this section, the basic concepts of drug concentration and drug action are followed by a review of the mechanisms of action of the major drug groups used in food animal practice including NSAIDs, glucocorticoids, reproductive drugs, antimicrobials, and parasiticides.
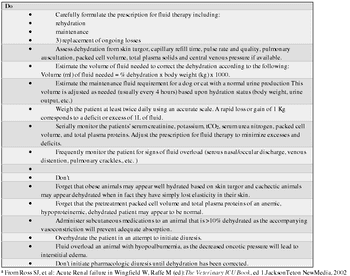
Fluid therapy is one of the most important aspects of patient management in veterinary medicine. It is however, important to realize that fluid therapy is a supportive measure and the underlying disease process that lead to aberrations in water, electrolyte and acid-base status must be identified and treated.
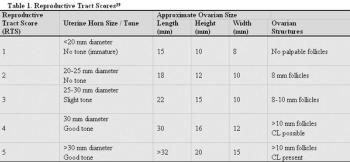
Productivity for beef cattle herds has been shown to be increased when a high percentage of heifers become pregnant early in the first breeding season. A producer's heifer selection and development program should result in most heifers in the replacement pool reaching puberty at least 42 days prior to the start of breeding because the conception success to first service is lower on the puberal estrus compared to the third estrus.

Many veterinarians express frustration when trying to provide their clients with the best advice on which diagnostic tests to recommend for purchased cattle or the resident herd. The goal is to screen apparently healthy cattle to identify carriers of infectious disease that could cause reproductive losses and other health problems in the herd.

Acute renal failure may be defined as an abrupt reduction in renal function resulting in accumulation of nitrogenous waste products and dysregulation of water, electrolyte, and acid base balance. Differentiating acute from chronic kidney disease is important for both therapeutic and prognostic reasons.

Enterotoxemia is characterized by proliferation of and exotoxin production by Clostridium perfringens in the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract. Although limited tissue invasion by the causative organism does occur, most local and systemic lesions result from the local and systemic effects of potent exotoxins produced by certain genotypes of this bacteria.

Maintenance of the physical and mental well being of animals within the shelter is a very important part of the stated mission for most sheltering organizations, yet surprisingly often stress reduction and enrichment to ensure good behavioral health is considered a luxury rather than part of basic care. An animal's behavioral health is a result of their genetic background, their learned behavior patterns as a result of previous experiences, and their environment.