Alan H. Rebar, DVM, PhD, DACVP
Articles by Alan H. Rebar, DVM, PhD, DACVP

Before considering pathologic cytology of lymph nodes, it is necessary to define normal lymph node cytology. Aspirates from normal lymph nodes contain mixed cell populations in which small lymphocytes are the predominant cell (>80 percent of all cells).

Accumulations of excessive fluid in the pleural, peritoneal, or pericardial space represent edema of these body cavities. As such, the dynamics of fluid accumulation are governed by Starling's law. In general, pleural, peritoneal, and pericardial effusions can result from either inflammatory or non-inflammatory causes.
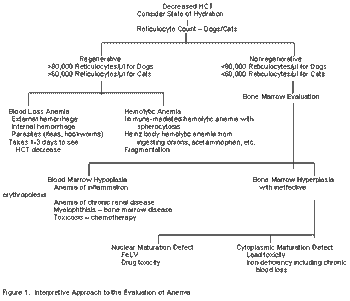
Hemograms consist of both quantitative data (total cell counts, differential cell counts, red cell indices, etc.) and qualitative data (blood film morphology). Proper interpretation depends on the integration of both.

Before considering pathologic cytology of lymph nodes, it is necessary to define normal lymph node cytology.

Hemograms consist of both quantitative data (total cell counts, differential cell counts, red cell indices, etc.) and qualitative data (blood film morphology). Proper interpretation depends on the integration of both.

Accumulations of excessive fluid in the pleural, peritoneal, or pericardial space represent edema of these body cavities.
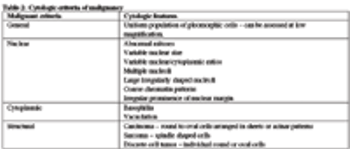
In the last ten years, exfoliative cytology has been gaining popularity as a diagnostic aid in veterinary practice.

The circulating white blood cells include the granulocytes, the monocytes, and the lymphocytes.

Nodules aspirated through the skin may be non-neoplastic, neoplastic but benign, or neoplastic and malignant.

Biochemical profiling may be defined as the use of multiple blood chemistry determinations to assess the health status of various organ systems simultaneously.
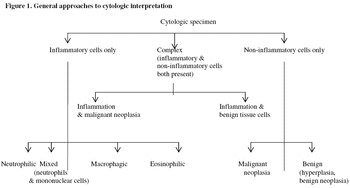
In the last ten years, exfoliative cytology has been gaining popularity as a diagnostic aid in veterinary practice.




