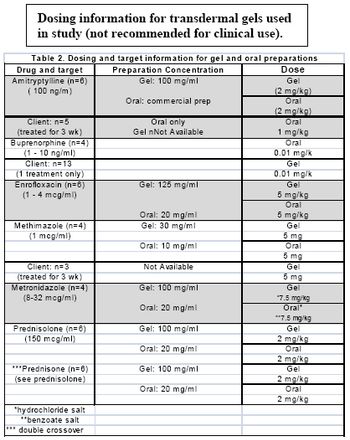
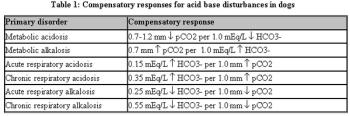
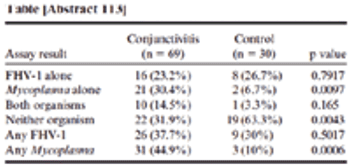
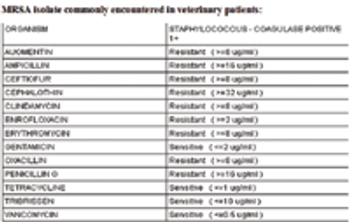
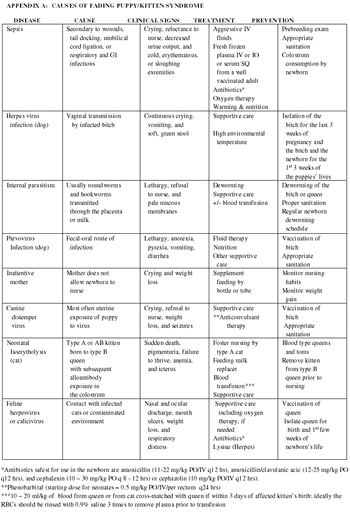
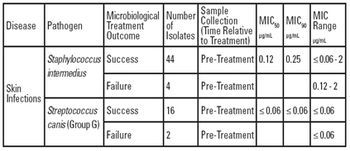
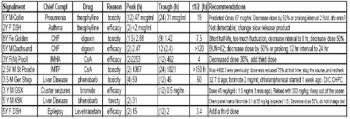
Vomiting is among the most common reasons that dogs and cats are presented for evaluation. Because there are a multitude of causes of vomiting, ranging from simple to complex, this can be a challenging problem for clinicians to accurately diagnose and manage.