
Although aspiration pneumonia is a common clinical diagnosis in dogs, studies on the causes, diagnostic findings, and outcome of affected dogs are sparse.

Although aspiration pneumonia is a common clinical diagnosis in dogs, studies on the causes, diagnostic findings, and outcome of affected dogs are sparse.

Acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) are challenging and frequently lethal respiratory disorders encountered in veterinary medicine.
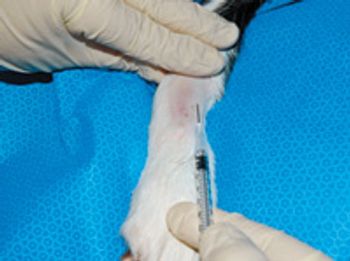
Follow these steps to acquire arterial samples to help diagnose acute lung injury or ARDS.

Guidelines for equine intra-articular therapy

Evaluation of the pet with respiratory disease may be challenging.

The pleural space is defined as the area between the lungs and the chest wall.

Feline upper respiratory infection (URI) is perhaps the most frustrating illness facing shelter veterinarians, managers and staff.

Traumatic thoracic injuries are prevalent in small animals, particularly in dogs.

Treating animals with respiratory distress may be very challenging.

Cough is a common presenting complaint for dogs and, to a lesser extent, cats.

Pulmonary edema is defined as the accumulation of abnormal amount of extravascular lung water.
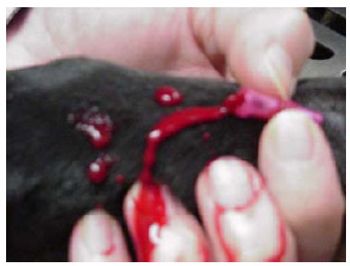
Blood gas, electrolyte and lactate analysis are very useful in management of the ill or injured dog or cat. Knowledge of normal values and what they indicate can help improve patient care and understanding of the pathophysiological changes accompanying critical illness.
Cats with respiratory distress represent a significant diagnostic and therapeutic challenge to the small animal veterinarian.

Respiratory emergencies should always be triaged quickly and with precision.

Initial triage evaluation of the post-trauma patient should include a careful evaluation of respiratory function.

Oxygen delivery to the tissues must be prioritized in any critical patient.

Nasal problems are a frequent reason for seeking veterinary care.

Respiratory dysfunction commonly occurs as a sequela of critical illness in dogs and cats.

Puppies are often physiologically stressed by changes in ownership and new environments.

Feline asthma arises from a heterogeneous and poorly characterized group of conditions of the bronchi.

Before we can start begin to review abnormalities in the lungs lets first do a review of normal anatomy.

Dogs and cats with partial or complete upper airway obstruction can present with varying degrees of dyspnea.

Coughing is a common presentation in small animal practice, which can be caused by either heart or respiratory tract disease.

Antibiotic therapy is obviously one of the most important modes by which bacterial infections are treated, and the lungs are no exception.

In most patients with pneumonia, antibiotic therapy should be considered part of an overall management scheme, rather than the only treatment.