
Bronchial obstruction can develop due to inflammatory infiltrates (eosinophils, neutrophils, or macrophages) or hypertrophy of bronchial tissues.

Bronchial obstruction can develop due to inflammatory infiltrates (eosinophils, neutrophils, or macrophages) or hypertrophy of bronchial tissues.
Air within the mediastinum may be the result of spontaneous rupture, trauma, or the result of diagnostic or therapeutic interventions.

Tracheobronchial disease represents a series of problems covering disorders of the upper and lower airways.

Diseases of the parenchymal lung tissue present a unique clinical problem. With impaired gas exchange and hyoxemia rapid diagnosis and treatment is essential.

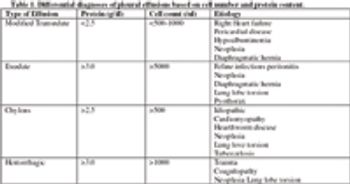
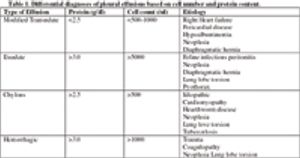
Respiratory distress cats can present a therapeutic dilemma. These small patients can be so severely compromised that diagnostics and treatment can stress them to the point of respiratory and cardiac arrest.

Pulmonary thromboembolism (PTE) is the occlusion of the pulmonary vasculature by products of the coagulation cascade.

The most common causes of chronic nasal discharge include neoplasia, aspergillosis or cryptococcosis, nasal foreign body, rhinitis secondary to dental disease, and idiopathic or inflammatory rhinitis.

While trauma by its very nature is a polysystemic disease, pulmonary complications present one of the most common, and life-threatening aspects of trauma triage.

Published: April 1st 2009 | Updated:
Published: April 1st 2009 | Updated:

Published: April 1st 2009 | Updated:

Published: April 1st 2009 | Updated:

Published: April 1st 2009 | Updated:

Published: April 1st 2009 | Updated: