Melissa Kennedy, DVM, PhD, DACVM
Articles by Melissa Kennedy, DVM, PhD, DACVM

FIP – nothing's ever simple....It is a multifactoral disease involving virus factors, host factors, and environmental factors. The virus of FIP is feline coronavirus (FCoV) – interestingly, it is required but not sufficient for FIP. Coronaviruses have a large RNA genome.

The primary role of the immune system is to protect against infectious disease. The mechanisms employed vary in efficiency for intra- vs extracellular pathogens. Nonspecific immunologic resistance involves interferon – stimulates production of proteins with antiviral activity.

Immunoprophylaxis is the enhancement of a specific immune response to the specific pathogen. Humoral and cell-mediated immune response are critical to effective immunity. This response is induced by microbes, their components or by-products. The majority of vaccines prevent infectious disease, but not infection.

An outbreak of respiratory disease occurred in a kennel of racing greyhounds in 2004. While some dogs exhibited mild disease with fever and cough, some experienced peracute death with pulmonary hemorrhage (case fatality 36%). Virologic analysis revealed an influenza virus that was later found to be closely related to equine influenza virus subtype H3N8, sharing >96% genetic sequence identity.

The immune system has two arms of defense, nonspecific and specific. As with the immune system in total, there are many elements of the nonspecific arm of the immune response. These have in common their lack of strict recognition of foreign material and absence of memory.

Immunology plays a huge role in diagnostics for infectious diseases. In addition, various assays are able to assess the immune system itself in an animal.

Molecular diagnostics have quickly become a mainstay in veterinary medicine, particularly in the area of infectious diseases. With the rapid advancement of technology, it is difficult to keep up with what is available as well as to understand what the results mean.

Why??? One of two goals: Enhancing the immune response (e.g. infection, cancer); or 2) suppressing the immune response (e.g. autoimmune disease). Results are often broad in scope, when usually we want a focused effect; for example, enhancing certain components of the immune response, like CMI in FIP, or suppressing only certain components of the immune response, like B lymphocytes that recognize an allergen, and produce IgE.

Feline herpesvirus (FHV) is a common pathogen of domestic cats. The virus is a ds DNA virus with a lipid envelope. The virus primarily targets epithelia of the upper respiratory tract and conjunctiva, and only rarely spreads beyond these regions to cause disease.

Feline infectious peritonitis (FIP) continues to be a significant disease in domestic cats.

An outbreak of respiratory disease occurred in a kennel of racing greyhounds in 2004.

Parvoviruses remain a significant enteric pathogen of cats and dogs.

Vaccination is an important tool in veterinary medicine, preventing disease and reducing virus circulation for many important viral pathogens.

Feline herpesvirus is a common pathogen of domestic cats.
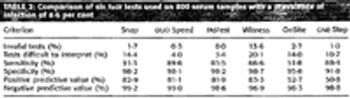
Feline leukemia virus (FeLV) remains a significant threat to cats.

Diagnosis of viral infections is an important component of small animal patient care.

Parvoviruses remain a significant enteric pathogen of cats and dogs.

Vaccination is an important tool in veterinary medicine, preventing disease and reducing virus circulation for many important viral pathogens.

An outbreak of respiratory disease occurred in a kennel of racing greyhounds in 2004.

Feline infectious peritonitis (FIP) continues to be a significant disease in domestic cats.

Feline herpesvirus (FHV) is a common pathogen of domestic cats.

Influenza virus is an ancient virus that has affected man for many centuries.


