
At birth the hips are normal. The femoral head and neck are cartilaginous and begin forming bone by endochondral ossification.

At birth the hips are normal. The femoral head and neck are cartilaginous and begin forming bone by endochondral ossification.

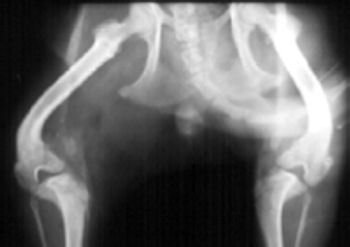
Coxofemoral luxation is the most commonly luxated joint in dogs, accounting for 90% of all luxations. It is usually the result of trauma or severe hip dysplasia with 78% being craniodorsally luxated.

At birth most hips are normal. The femoral head and neck are cartilaginous and begin forming bone by endochondral ossification.

Physical rehabilitation is becoming a common place therapy in veterinary medicine. Several benefits have been proven and continue to be elucidated.

Incorrect answer for Image Quiz: Dermatology-A dog with a suddenly crusty, itchy muzzle
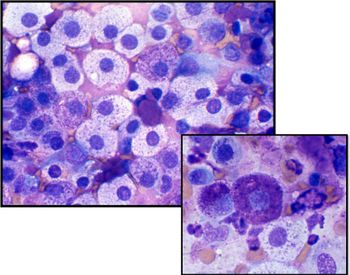
Correct answer for Image Quiz: Cytology-A subcutaneous mass in a senior dog

Answers to frequently asked questions you need to know.

These D.I.Y. slings can help your patients with limited mobility.
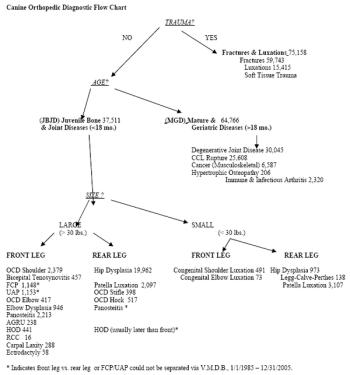
Orthopedic diseases in dogs account for ~22% of all small animal diagnoses, based on the Veterinary Medical Data Base. The canine orthopedic diagnostic flow chart presented here (Figure) is a useful tool for diagnosing orthopaedic diseases in dogs by guiding the clinician to the most likely and logical group of diagnoses.
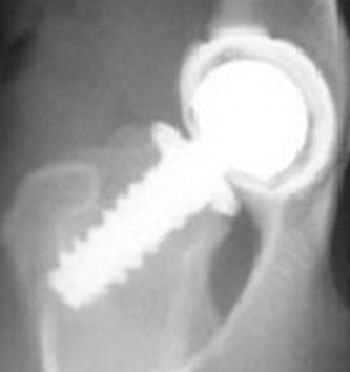
CHD has been called inherited, a developmental disease, and most accurately in the author's opinion, a "moderately heritable disease". CHD is a multifactorial disease with part of its cause being from genetic influences (estimated at 25%-80%) and part from environmental influences.

Conservative treatment of CCL rupture is the same as treatment for DJD: exercise to build muscle, weight control and medications such as NSAID's and Adequan. Surgery is the most effective treatment for CCL tear if done before DJD is established. Conservative treatment is indicated if surgery is not chosen by the owner because of cost or other reasons.
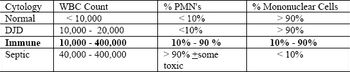
Synovial membrane lines all diarthrodial joints. Synoviocytes are macrophage like cells which phagocytize foreign materials and produce synovial fluid which contains the two lubricants hyaluronic acid and polysulfated glycosaminoglycans. The normal synovial membrane is a poor filter, allowing all components of blood into the joint fluid except cells, platelets, and large molecules such as fibrinogen.
OCD of the hock occurred bilaterally in 42% of the reported cases. The lateral trochlear ridge is involved in 25% of the cases and the medial trochlear ridge in 75% of the cases.

The best treatment for degenerative joint disease is prevention, by removing the inciting cause before DJD is established if at all possible (TPO, JPS, cruciate stabilization, patella stabilization, etc.) Irreversible changes of DJD (visible in the form or periarticular osteophytes) are present by 28 days after the cause is present.
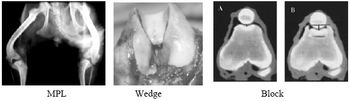
The patella is a type A (primary function is articulation) sesamoid bone located in the tendon of insertion of the quadraceps muscles. The origins of the quadriceps muscles are the proximal femur and immediately cranial to the acetabulurn (rectus femoris m.). The quadriceps m. follows a straight line, by necessity, to its insertion at the tibial crest.
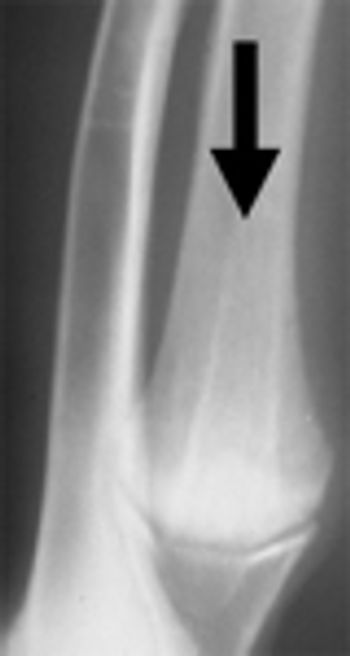
Agenesis and malformation of the phalanges, metacarpal and carpal bones in utero is the basic pathology, and is occasionally accompanied by subluxation of the elbow.
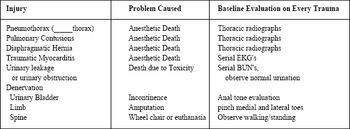
Thorax: Many dogs with pneumothorax (hemothorax, chylothorax, diaphragmatic hernia, etc) are able to ventilate marginally but adequately when at rest in a cage. The loss of lung/ventilation capacity may not become clinical for several minutes after induction of general anesthesia or during recovery.

New information on treating medial patellar luxation in dogs.

Watch our August 2011 issue for results of the survey.


Orthopedic infections should also be thought of as infections involving the bones (osteitis or osteomyelitis), joints and surrounding support structures (periostitis, myelitis, cellulitis). Typically when we think of orthopedic infections we think of infections resulting after orthopedic surgery.

The coxofemoral joint is a ball and socket joint. Normal stability of the hip is provided through a combination joint capsule, ligament of the head of the femur and dorsal acetabular rim. In addition, the joint fluid and acetabular labrum including the ventral acetabular ligament and extraarticular soft tissue structures such as the gluteals, adductors and abductors of the hip joint provide secondary stability.

There are more and more options out there for our patients in the way of braces, orthotics and assistive devices. They can provide much needed help during or after rehab, surgical recovery, as an alternative to surgery and our geriatric patients.

The goal in management of open fractures is to prevent further contamination, prevent additional damage to the bone and surrounding soft tissues especially nerve and vascular supplies and facilitate timely stabilization.

The workload of a police dog or a bird dog creates varying medical issues which can be dependent upon their physical condition. If they are not conditioned to handle the workload exertional medical problems can arise. Another cause of medical problems in these dogs is related to the environments in which they work.