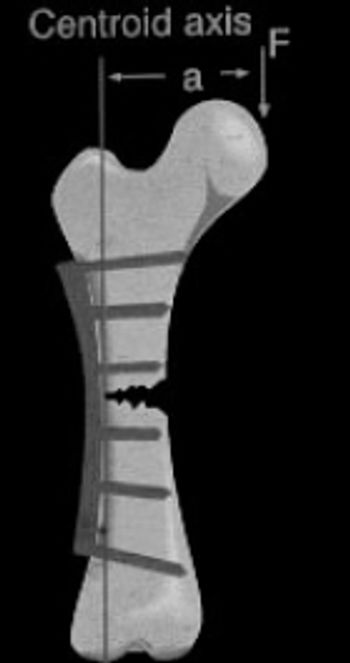
The most significant change in recent years in the management of fractures has been the more recent emphasis on "biologic fixation" as opposed to "mechanical fixation". The latter refers to the direct fixation techniques whereby fractures are reconstructed anatomically, and the former refers to indirect fixation techniques whereby the fractures are spanned (or "bridged").