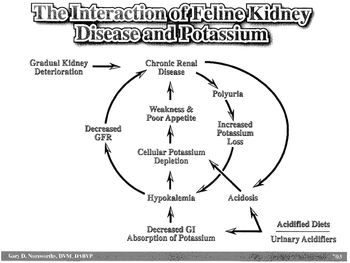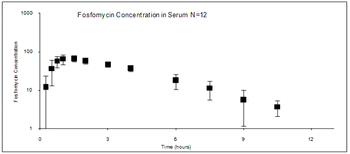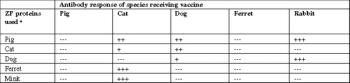
Sterilization = any procedure that makes an individual incapable of reproduction - Castration and vasectomy are reported techniques in males and ovariohysterectomy, ovariectomy, and tubal ligation are reported techniques in females. Castration and ovariohysterectomy are the most common surgical sterilization methods in the United States.