
Food allergy in horses is a confusing, poorly understood and sometimes controversial topic.

Food allergy in horses is a confusing, poorly understood and sometimes controversial topic.

Check out these best practices for choosing dental sutures, needles and suturing methods.

While this document does not address equipment such as syringes, needles and radiographic units, it does focus on devices marketed in the liquid form, for use exclusively within veterinary medicine.

Dr. Susan E. Little address the epidemiology and treatment of this tick-borne disease.
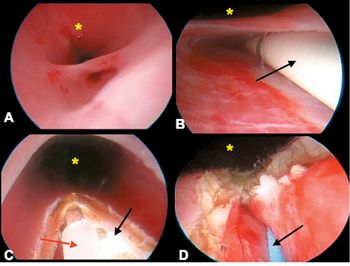
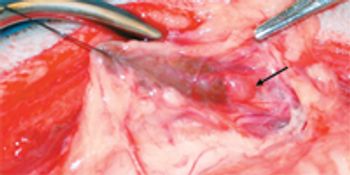
Cystoscopic-guided laser ablation is a minimally invasive alternative to surgery for these congenital anomalies.

Dundas, Ontario - The World Small Animal Veterinary Association (WSAVA) crafted a set of global nutrition guidelines consistent with those released last year by the American Animal Hospital Association (AAHA).
This condition may be more common than you think, so evaluate all dogs with increased calcium concentrations.

Durango, Colo. - About 150 dogs in Durango, Colo., have fallen ill with one local veterinarian can only call a "mystery."

First, a word of caution.... Assess each individual situation carefully and remember that anything can be dangerous in the right quantity (even water). Also, consider health status of patient. Once you take all these into account, there are many exposures that you may be able to talk clients through managing at home.

Case 13: 12 year old labrador retriever, pre-dental workup reveals ALT 250, alkaline phosphatase 355, BILIRUBIN 0.2.

It is important that the clinician formulate a treatment protocol based on a correlation of clinical course, laboratory and gross findings, and histologic findings rather than relying on histologic changes alone. Although treatment principles for cats and dogs with IBD are similar, drug selection and dosage regimens vary between these two species in some situations.

Immune suppression is the cornerstone of the treatment of IMHA. Commonly used medications include corticosteroids, azathioprine, and cyclosporine. Side effects can occur because of the medication used or could be from the immune suppression itself. To date there is little data on the incidence of side effects in dogs treated for IMHA.

Antibiotic therapy is indicated for treatment of suppurative hepatitis, cholangiohepatitis and hepatic encephalopathy, and prevention of septicemia. The bactericidal function of the hepatic reticuloendothelial (RE) system may be compromised in hepatic disease, especially if hepatic blood flow or oxygen tension is altered, resulting in septicemia.

Brucella canis is a non-motile, Gram negative coccobacillus with a host range limited to domestic and wild canids. Stray dog populations may act as a reservoir. There is a higher reported prevalence in purebred animals but few studies have attempted to compare populations of owned and stray dogs.

Intestinal biopsy may be accomplished two ways: endoscopy and surgery. CBC, serum chemistry profile, and urinalysis are useful and may point out systemic manifestations of the disease which will aid in correctly diagnosing and prognosing the problem (e.g., hypoalbuminemia due to histoplasmosis), but are also useful as a preanesthetic work up before endoscopy.

Methanol (also known as methyl alcohol or wood alcohol) is found most commonly in "antifreeze" windshield washer fluid and varies in concentration from 20-100% (with 20-30% being the most common form.) Methanol's metabolite, formaldehyde, is rapidly oxidized by the enzyme aldehyde dehydrogenase to formic acid, which can cause metabolic acidosis if significant quantities of methanol are ingested.

Average puppy and kitten deaths during the first 12 weeks of life approach? 11%-34%. Still births or death within the first 24 hours account for 5% of the losses; an additional 5% loss occurs during the neonatal period; and 0%-5% loss in transitional & socialization periods. Infectious diseases are not the most common cause of neonatal or transitional period mortality.

Diagnostics for chronic gastrointestinal problems include a complete blood count (including manual differential), biochemical profile, urinalysis, fecal flotation (+/- direct examination, fecal cytology, sedimentation, acid-fast staining, occult blood, PCR testing for parasites), thoracic and abdominal radiographs and abdominal ultrasound. Trypsin-like immunoreactivity may be indicated.

The procedures discussed will include in-hospital urine cultures, voiding urohydropropulsion, and esophageal feeding tube placement.

Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) currently is recognized as a common and important medical problem in cats. Three general types of clinical presentations have been identified in cats with idiopathic IBD: (1) a clinical course characterized primarily by vomiting, (2) a clinical course characterized primarily by diarrhea, and (3) a clinical course that includes both vomiting and diarrhea as primary signs. Associated clinical signs can include change in appetite (anorexia, inappetence, or ravenousness), weight loss, and lethargy. In some cats, the clinical signs are cyclic; they seem to flare up and then abate in a predictable pattern.

It is known that high blood pressure is associated with renal disease in many species including cats and dogs. That this is important is known from many studies including ones involving dogs.

Case 8: 6 year old dog on phenobarbital. ALK PHOS 2000, ALT 120, BILI 0.2.

The neonatal period is the first 4 week of life. During this critical period, the puppy or kitten has a different physiology and rate of development and than during the rest of the pediatric period. Once the puppy or kitten is 6- 8 weeks of age, then all of the development is complete and the youngster can be considered a "growing" adult.

Initial nonspecific management of vomiting includes NPO (in minor cases a 6-12 hour period of nothing per os may be all that is required), fluid support, and antiemetics. Initial feeding includes small portions of a low fat, single source protein diet starting 6-12 hours after vomiting has ceased.

Aging in dogs and cats is associated with gradual and progressive deterioration in the delicate body systems that eventually results in anatomical changes and decreased physiological functions. At some stage in the progressive decline, a "tipping point" is reached, where all of the physiological reserves are exhausted resulting in altered biochemical parameters; overt changes in diagnostic screening tests; and/or the onset of clinical symptoms of age-related disease occurs.

It is always important to document and handle all materials related to a case as evidence. Often, however, situations arise when veterinarians only later realize that they were witness to an abuse case.

Icterus is a term used to describe the clinical appearance of hyperbilirubinemia. While reference values may vary, in most instances a serum bilrubin > 1 mg/dl is considered abnormal but clinically detectable icterus usually does not occur until the bilirubin is > 3 mg/dl.

A range of behaviors harmful to animals may be defined as abuse. This includes both intentional and unintentional harm or neglect. Animal cruelty statutes exist in all 50 states, but legal definitions of cruelty vary.

Nasal discharge is seen most commonly with diseases of the nasal passages, sinuses and nasopharynx. Occasionally disease involving the lower airways (trachea, bronchi, etc) can result in nasal discharge.

The fungal organisms most commonly associated with systemic disease are Blastomyces dermatitidis, Histoplasma capsulatum, Coccidioides immitis and cryptococcosis.