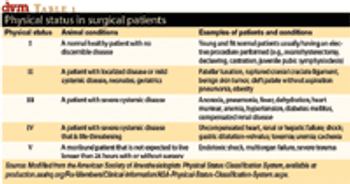
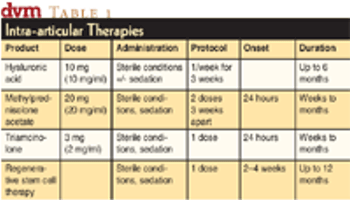
A working definition of antimicrobial prophylaxis in surgery is the administration of an antimicrobial drug to a patient, in the absence of infection, prior to surgery. The history of the use of these agents during surgery is interesting and reveals many of the problems which occur with their use.