
Canine Hyperadrenocorticism (Canine Cushing's syndrome) is one of the more common endocrinopathies encountered in small animal practice; ranking behind only hypothyroidism and diabetes mellitus.

Canine Hyperadrenocorticism (Canine Cushing's syndrome) is one of the more common endocrinopathies encountered in small animal practice; ranking behind only hypothyroidism and diabetes mellitus.

Hyperthyroidism is the most common endocrine disorder in the cat. Since being first recognized in 1977, the incidence has increased steadily. This is, no doubt partly due to greater awareness and early screening, but certainly also due to a real increase in occurrence of this disease.

The pituitary gland is a small structure that adheres to the base of the diencephalons; just caudal to the optic chiasm. It is comprised of an anterior portion-the adenohypophysis(which is made up of the pars distalis and the pars intermedia) and a posterior portion termed the neurohypophysis (pars nervosa).

Management of the uncomplicated feline diabetic can occasionally be controlled by oral hypoglycemic agents (approximately 25-35%). This is because approximately 90% of the feline diabetic patients are similar to human Type2 diabetes mellitus (non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus-NIDDM). However, by the time the cat is diagnosed with diabetes mellitus, the blood glucose is severely elevated (often>450 mg/dl) and many cats are ketotic, thus insulin is usually required.

The thyroid gland is made up of paired lobes on the ventrolateral surface of the proximal trachea. Felines may have accessory thyroid tissue in the neck and thorax. The size of the thyroid gland varies with the size of the dog; with medium-sized dogs having lobes approximately 5 cm. in length, 1.5 cm. in width, and 0.5 cm in thickness. In the average (4.5 kg) cat each lobe is approximately 2 cm.

Dogs with gallbladder mucoceles should be tested for other common endocrine diseases.
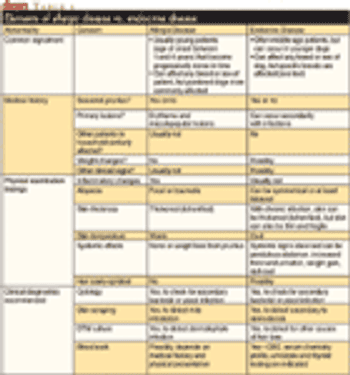
A look at dermatologic disorders associated with endocrine disease.

Use these resources to communicate to communicate to clients about the disease.

A new study investigates the most efficient protocol for determining the degree of adrenocortical insufficiency or critical illness-related corticosteroid insufficiency in cats.

Why ACTH stimulation testing is indicated in patients with possible renal disease.

How stress affects blood glucose concentrations.

This online on-demand archived Webinar provides an overview of the available diagnostic tests for canine hypoadrenocorticism and hyperadrenocorticism. Current treatment recommendations including therapeutic monitoring protocols will also be reviewed. (1 CE credit)

Rockville, Md. -- The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) reports there will be a shortage of Vetsulin (porcine insulin zinc suspension), a product used to treat diabetes mellitus in dogs and cats.
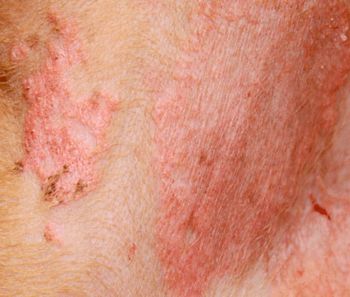
What condition do these skin lesions most likely represent?

What dietary intervention might improve a diabetic cat's chances of resolution?

Why sterile saline solution may be better than sterile water.

In general, we try to regulate the diabetes before attempting to diagnose hyperadrenocorticism.

In this online on-demand archived Webinar, Dr. Nelson reviews the clinical manifestations and criteria used to establish a diagnosis of feline hyperthyroidism. He examines the interpretation of thyroid hormone test results and the diagnostic options for occult hyperthyroidism. (1 CE credit)

This online on-demand archived Webinar provides an overview of the available diagnostic tests for hypothyroidism. Current treatment recommendations including, therapeutic monitoring protocols, are reviewed. (1 CE credit)


How would you help this cat with two serious conditions?

This study demonstrated that short-term administration of glucosamine-chondroitin sulfate does not significantly affect serum fructosamine concentrations in healthy dogs.

Researchers recently investigated the accuracy of a single cortisol concentration measurement to monitor dogs receiving trilostane for hyperadrenocorticism.

An important tip concerning insulin administration by clients.

How can a dog's weight affect insulin therapy?