Cynthia Ward, VMD, PhD, DACVIM
Articles by Cynthia Ward, VMD, PhD, DACVIM

Diabetes Mellitus (DM) and hyperadrenocorticism (HAC) are common endocrinopathies in dogs that often occur simultaneously in the same patient. Diagnosis and management of concurrent disease may be a challenge to the practitioner since many clinical signs of DM and HAC are similar.

Pathogenesis: Insulin-dependent, non-insulin dependent, and transient

Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis--classic endocrine feedback loop

Thyrotoxicosis is a term used to describe any condition in which there is an excessive amount of circulating thyroid hormone whether from excess production and secretion from an overactive thyroid gland, leakage from a damaged thyroid gland, or from an exogenous source.

Ketone bodies: acetoacetate, beta hydroxybutyrate, acetone

Hyperadrenocorticism is a common endocrinopathy in middle to older aged dogs. Common clinical signs to make the clinician suspicious of hyperadrenocorticism include polyphagia, polyuria/polydipsia, pyoderma, pot bellied appearance, and persistent urinary tract infections.

Canine hypothyroidism is the most commonly diagnosed endocrinopathy in the dog. There is a large incidence of false diagnoses and unnecessary supplementation.


Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas
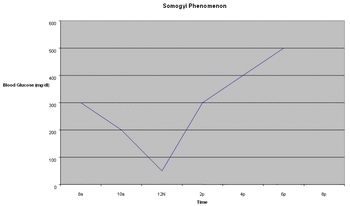

Pathogenesis: Insulin-dependent (rare), non-insulin dependent, transient, How do you distinguish, does it matter.

Hyperadrenocorticism: a rare disorder in
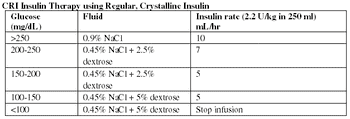
Pathophysiology: Ketone bodies: acetoacetate, beta hydroxybutyrate, acetone
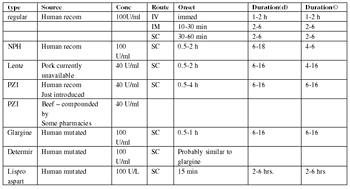
Insulin treatment options for diabetic cats.
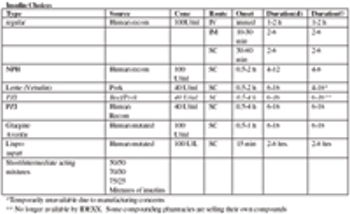
Pathogenesis: Insulin-dependent, non-insulin dependent, transient

Start insulin therapy?now what?

Clinical signs: polyphagia, polyuria/polydipsia, pyoderma, pot-bellied appearance, urinary tract, and infection

Diseases of the Adrenal Cortex and how to diagnose them

Small animal patients presenting with a primary complaint of hypercalcemia can often be a diagnostic challenge. Typically, the clinical signs are insidious and nonspecific.

When to suspect your diabetic is also Cushinoid

One of the most common endocrine disorders of dogs is hyperadrenocorticism (HAC). Clinical disease results from excess secretion of hormone from the adrenal cortex.
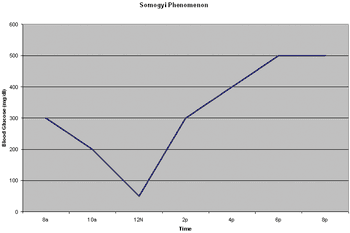
The basal T4 concentration is useful in most cases.

Risk factors, signalment, diagnosis, treatment objectives, and prognosis for cats with pancreatitis.

Antithyroid medications, organic iodine compounds, surgery, 1311, percutaneous ethanol, and adjunct therapies.
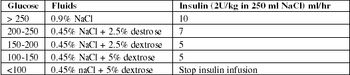

Cats presenting with a primary complaint of hypercalcemia can often be a diagnostic challenge.

Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and patient evaluation for a diabetic cat.

Understanding hyperadrenocorticism and hyperaldosteronism
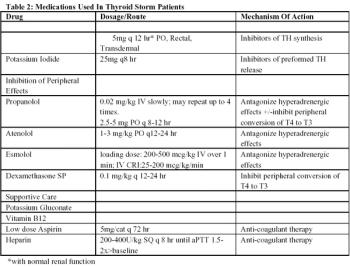
Clinical signs, clinicopathologic abnormalities, diagnosis, and treatment.











