
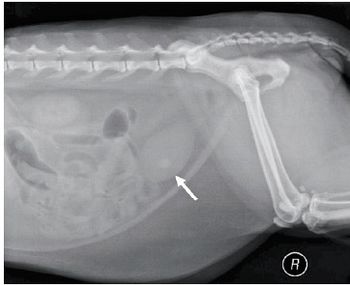
The most common presentation of salivary mucoceles in cats isn't cervical swelling.

The most common presentation of salivary mucoceles in cats isn't cervical swelling.

One of the biggest risk factors for this condition in cats.

Tips for performing an ultrasonographic examination on cats with chronic renal disease.
Dr. Carl Osborne examines feline urolith composition over the past three decades.

For problems with an underlying behavioral cause, try these options.

A look at the role of dietary fat in chronic diarrhea in cats.

Find out when practitioners should recommend surgery.

What you can do to reduce recurrence following feline inflammatory polyp removal by traction.

A recent study examined two treatment options for the tick-borne illness.

Teach cat owners how to recognize subtle signs of feline illness.

How--and how often--uveitis can lead to secondary glaucoma.

Chapter 8 of a nine-part video series about the Veterinary Care Usage Study by Dr. Karen Felsted, CEO of the National Commission on Veterinary Economic Issues.

The most common concern expression by clients about their cats' behavior involves inappropriate elimination.

It's not a glamorous title, but polishing your communication skills can help attract business from clients whose cats experience litter box problems.

Learn the signs and common treatments for the chronic and acute complications that may develop so you can help catch them early in your feline patients.

The real reasons behind one of the veterinary industry's biggest problems.

National Report - Nearly one-third of the veterinary professionals surveyed don't typically bring their own cat in for an annual wellness examination.

Does the obesity paradox in people occur in cats as well?

When trying to identify mild degrees of adrenocortical insufficiency or critical illness-related corticosteroid insufficiency, low-dose ACTH stimulation testing is necessary to achieve an accurate diagnosis. But what dose is best in cats?

One of the scariest tick-borne pathogens is Cytauxzoon felis.

Dr. Daniel Carmichael helps a reader address this frustrating condition.
What/who is a cat? What characteristics make this species different from us or from dogs? By understanding our feline patients better, we can provide a better experience and environment for them. The basis of working cooperatively with cats is empathy based on an understanding of their nature and behaviours and trying to imagine what their experience is like.
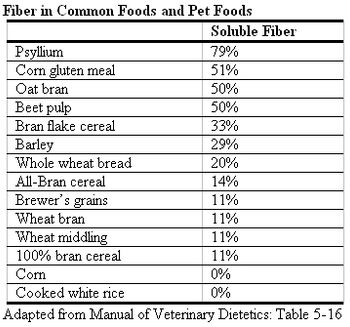
Constipation is defined as the infrequent or difficult evacuation of stool. It is a common problem in cats that may be acute or chronic and does not inherently imply a loss of colonic function. Often the underlying cause is dehydration and is readily managed by supportive hydration, by oral, nutritional or parenteral means.

It is the rare adult who does not have an emotional response to thoughts of dying. We are all inherently aware of our mortality and to that of those around us. No different from our clients, we fear the pain and suffering of friends and companions, human or non-human.

Permethrin, a synthetic type I pyrethroid, is found in many flea and tick shampoos, dips, foggers, spot-ons, and sprays as well as many household and yard insecticide formulations. While permethrins have a relatively wide margin of safety in dogs, cats appear to be more sensitive to the toxicity of concentrated permethrins.