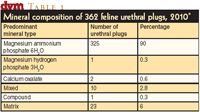
What characteristics make this species different from us or from dogs? By understanding our feline patients better, we can provide a better experience and environment for them. The basis of working cooperatively with cats is empathy based on an understanding of their nature and behaviours and trying to imagine what their experience is like.