
Your clients are confused and anxious and they want answers. Use this free team training to take the trauma out of the talk.

Your clients are confused and anxious and they want answers. Use this free team training to take the trauma out of the talk.

The hormones, which come from items made with livestock gullets, can cause hyperthyroidism in veterinary patients.
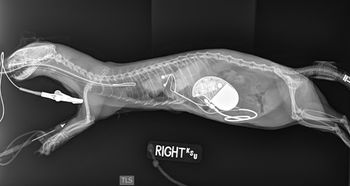
Here's an update on adrenal disease therapy for these more unusual veterinary patients, plus the adventure of Zelda, a rare recipient of a pacemaker thanks to Kansas State University.

While theres no cure for this adrenal condition, cats can achieve their full life expectancy with appropriate treatment.

According to CVC speaker and expert Dr. Chen Gilor, veterinarians should be screening more patients for hypoadrenocorticism or risk missing a diagnosis.

Injecting a dose of reality for veterinary clients with diabetic cats isn't painful-it's positively inspiring!

Spend a little time educating these veterinary clients and help them avoid errors.

Each Veterinary Medicine Essentials package covers diagnostic steps, treatment plan guidance and the latest updates, plus resources to share with your entire veterinary team and your clients.

Each Veterinary Medicine Essentials package covers diagnostic steps, treatment plan guidance and the latest updates, plus resources to share with your entire veterinary team and your clients.

Each Veterinary Medicine Essentials package covers diagnostic steps, treatment plan guidance and the latest updates, plus resources to share with your entire veterinary team and your clients.

From image quizzes to journal reviews and updated protocols, heres what your colleagues couldnt get enough of this year.

These two quick tips from Dr. Chen Gilor will help you more readily identify affected dogs.

Use these communication techniques to talk about a chronic but treatable disease like Cushing's.

Ohio State researcher optimistic that monthly injections could replace daily insulin in cats.

You want to inspire careful home care and calibrate expectations for the owners of diabetic cats and dogs. And as with many things, it starts with conversations between veterinary team members and pet owners in the exam room ...

Sweet! Hacks for overcoming everyday challenges with this common endocrine disease.

Reader says vomiting isn't a major sign in feline pancreatitis. Our feline expert agrees.

This handout gives your clients the information they need about the cost and tests involved in managing their pet's chronic disease.

Let Dr. David Bruyette keep your cortisol concentrations from rising with these tips for confirming hyperadrenocorticism in dogs.

Dr. David Bruyette, AKA "Dr. Endocrine," is back with the basics (and a bit more) on treating this sometimes tricky disease.

Let's head back to the halls of the University of Tennessee's College of Veterinary Medicine to help save this dog with a palpable thyroid mass.

This diabetic dilemma is a pain, Highness. Anyone who says differently is selling something.

A comprehensive guide to the diagnosis and treatment of this common veterinary endocrine disease.

Why you may be seeing more cases, better insight into causes and best treatment practices-plus exclusive bonus material on Dr. David Bruyette, the Cushing superfan.
Identification may be found in the difference in glucose concentrations between veterinary patients plasma and peritoneal fluid.