
The principles of management of patients with severe lung disease and injury are summarized and the cases depicting the use if these management techniques are presented.

The principles of management of patients with severe lung disease and injury are summarized and the cases depicting the use if these management techniques are presented.

Critical care includes around-the-clock nursing and support for vital organ function.

It is important to remember that pain is an experience, not a neurologic process.
It is suspected that mammals generally adopt a respiratory pattern that meets their metabolic needs with the least metabolic energy cost.
When first alerted to a patient presenting in crisis, the goal of the initial examination is to rapidly identify any imminently life-threatening problems via a streamlined, efficient, clinical examination.

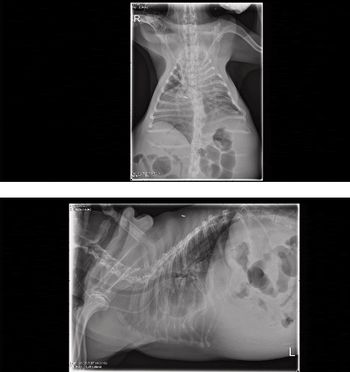
While trauma by its very nature is a polysystemic disease, pulmonary complications present one of the most common, and life-threatening aspects of trauma triage.

Davis, Calif. -- Earthquakes and fires happen often enough in the state that the University of California, Davis is developing a program to offer large-animal emergency response training.

We experience veterinary emergencies on a weekly, if not daily, basis. Rapid and accurate patient assessment, diagnostic imaging interpretation and treatment can be the difference between patient survival and death.

We experience veterinary emergencies on a weekly, if not daily, basis. Rapid and accurate patient assessment, diagnostic imaging interpretation and treatment can be the difference between patient survival and death.

Dyspneic cats are frequently presented to clinicians as emergencies. Because they are fragile and very easily stressed, it is a good idea to have a planned, rational and quickly implementable strategy for their management.

Pain is defined by the International Association for the Study of Pain as an unpleasant sensory or emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage or described in terms of such damage.

Respiratory changes occur frequently in small animal patients. It is important to recognize, however, that not all changes in respiration are caused by disease of the respiratory system.

Initial triage evaluation of the post-trauma patient should include a careful evaluation of respiratory function.

Diabetic ketoacidosis is one of the more common endocrine emergencies seen in veterinary emergency centers throughout the US.

Acute respiratory distress (ARD) is the sudden onset of rapid and/or labored respiratory.
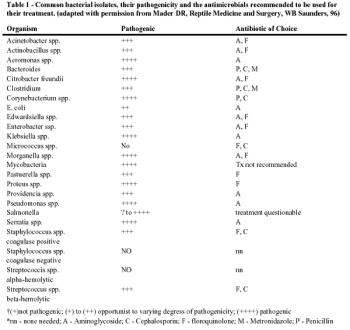
To date there have been very few pharmacokinetic studies published in reptiles, and with only limited numbers of antibiotics.

Paradise, Calif. - Thick smoke forced him from his home, but it hasn't kept Dr. Mike Seely from visiting a local evacuation shelter where he checks on hundreds of pets and livestock displaced by the wildfires that burn throughout California.

Although floodwaters receded along the banks of the Mississippi, the aftermath will continue to be felt for months and even years.

Nutritional needs often play a secondary role to medical and surgical intervention. Critically ill veterinary patients are at high risk for malnutrition because of physical impediments, as well as physiologic and metabolic abnormalities. Protein and/or calorie malnutrition results in decreased immune competence, decreased tissue synthesis, increased protein degradation (especially that of the lymphatic system), altered drug metabolism and is known to increase morbidity and mortality in human patients. Although veterinary studies are lacking, it is generally accepted that early enteral nutrition decreases complications from malnutrition.

A refurbished ambulance transfers referral patients between WestVet Emergency Center in Meridian, Idaho, and nearby practices.

Traumatized small animal patients represent a population in which a standardized approach to diagnosis centered on thorough background knowledge of traumatic injuries coupled with a complete physical examination will allow for rapid therapeutic interventions and optimization of patient care.
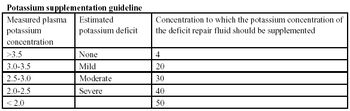
Potassium concentration is very commonly abnormal in critically ill patients.
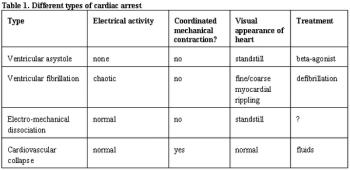
Veterinary and human studies cite a 30 to 60% rate of return of a spontaneous beating heart.

Plasma might be administered for its albumin or coagulation factor content.

The pH is a logarithmic representation of the hydrogen ion activity. It is an overall representation of the net effect of all of the acidotic and alkalotic processes in the body.