
Pain is defined as an aversive sensory and emotional experience.

Pain is defined as an aversive sensory and emotional experience.
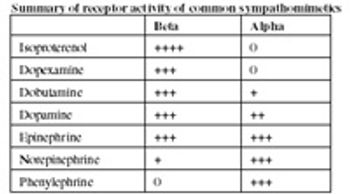
All commercially available sedatives and anesthetics are safe when properly administered to normal animals.
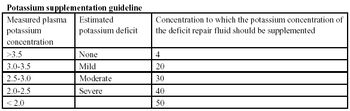
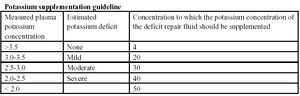
Potassium concentration is very commonly abnormal in critically ill patients.
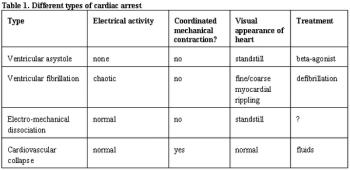
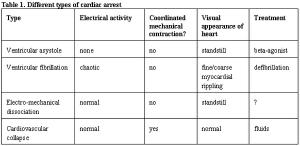
Veterinary and human studies cite a 30 to 60% rate of return of a spontaneous beating heart.

Plasma might be administered for its albumin or coagulation factor content.

The pH is a logarithmic representation of the hydrogen ion activity. It is an overall representation of the net effect of all of the acidotic and alkalotic processes in the body.

Animals are sometimes presented with such severe abnormalities in important blood constituents that a generic fluid plan does not adequately address the problem.
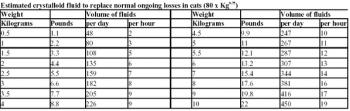
Once life-threatening hypovolemia and electrolyte problems have been corrected or if they were not judged to be present in the first place, the remaining fluid and electrolyte abnormalities can be dealt with.
"Preload" parameters are those which address whether or not the heart is receiving a venous return sufficient to expect reasonable forward blood flow.
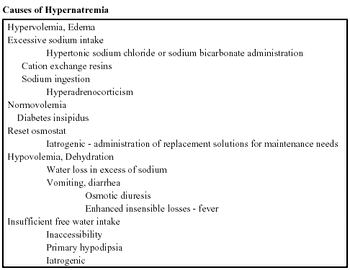
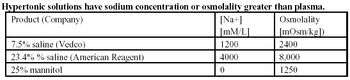
Sodium concentration is an expression of the relative numbers of sodium molecules to water molecules, irrespective of the total numbers.
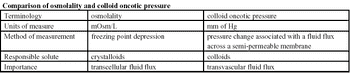
There are three major body fluid compartments in the body: intravascular, interstitial, and intracellular.

Published: April 1st 2008 | Updated:
Published: April 1st 2008 | Updated:
Published: April 1st 2008 | Updated:
Published: April 1st 2008 | Updated:

Published: April 1st 2008 | Updated:

Published: April 1st 2008 | Updated: