
Dr. Kristy Dowers shows you how to handle six common poisonings in cats.
Department of Clinical Sciences
College of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences
Colorado State University
Fort Collins, CO 80523

Dr. Kristy Dowers shows you how to handle six common poisonings in cats.

Over the last several years, there has been a shift in the mineral content of uroliths in cats from predominantly magnesium-ammonium phosphate (MAP) to calcium oxalate (CaOx). Of the nephroliths and ureteroliths analyzed by the Minnesota Urolith Center in 2002, 70% of 170 renolith submissions and 98% of ureterolith submissions were CaOx.

When hyperthyroidism was first reported in cats as a disease entity approximately 25 years ago, the majority of cases were advanced. The cats were thin, aggressive, polyuric, polydipsic, polyphagic and had large palpable goiters.

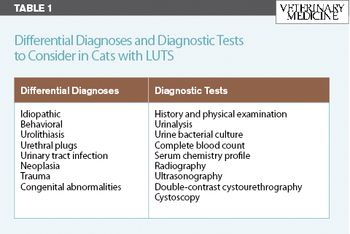
FLUTD refers to a spectrum of diseases that result in pollakiuria, hematuria, stranguria, dysuria and/or periuria in the cat. Common causes of these clinical signs include urolithiasis, urethral plugs and neoplasia (most commonly, transitional cell carcinoma).

Anemia is a common blood work abnormality in many species, including cats. Determining the regenerative nature of the anemia guides the workup of the case. Regenerative anemias suggest blood loss or red cell lysis. Red cell lysis can be due to toxins, infectious agents, neoplasia (as a secondary immune-mediated phenomenon) or primary immune-mediated hemolytic anemia.

Cats presenting with pleural effusion are nearly always in respiratory distress, ranging from an increased respiratory rate and effort to open mouth breathing. In the latter situations, therapeutic intervention must be initiated quickly to prevent respiratory arrest. The therapeutic intervention also provides your first diagnostic test.

Bartonellosis is an important emerging disease in humans and has been recognized to cause clinical disease in several other species, including dogs and cats. Bartonella henselae is the primary etiologic agent in Cat Scratch Disease, which causes fever and lymphadenopathy in humans.

These metabolic strategies mean that they are less efficient at "sopping up" post-prandial glucose loads that occur with high carbohydrate meals. Commercial dry diets, by virtue of the processing that must occur to create a dry diet, contain higher quantities of carbohydrates than the comparable canned diet.

Knowledge of breed predispositions and inherited disorders can direct your differential diagnoses and your diagnostic plan. For some of these diseases the genetic mutation has been identified and tests for the defect have been developed. For others, the phenotypical characteristics have been well-described but the genetic basis and mode of inheritance are unknown.

Cats are great patients because they are less likely to ingest large amounts of bad stuff just because. However, their unique metabolism presents other challenges as it contributes to the toxicities that we do see in cats and changes, often lowering, the toxic dose we can expect. Also, substances that are safe in other species can be deadly in cats.

Cats are true carnivores and as such have a metabolism specifically adapted to high protein meals.

FLUTD refers to a spectrum of diseases that result in pollakiuria, hematuria, stranguria, dysuria and/or periuria in the cat.

When hyperthyroidism was first reported in cats as a disease entity approximately 25 years ago, the majority of cases were advanced.

Over the last several years, there has been a shift in the mineral content of uroliths in cats from predominantly magnesium-ammonium phosphate to calcium oxalate.

Anemia is a common blood work abnormality in many species, including cats. Determining the regenerative nature of the anemia guides the workup of the case.

Bartonellosis is an important emerging disease in humans and has been recognized to cause clinical disease in several other species, including dogs and cats.
Researchers have yet to pin down the cause or causes of this frustrating and often painful disease, so a definitive treatment protocol remains elusive. Current recommendations include lifestyle changes such as stress relief and increased water intake.

Bartonella henselae is the primary etiologic agent in Cat Scratch Disease, which causes fever and lymphadenopathy in humans.

FLUTD refers to a spectrum of diseases that result in pollakiuria, hematuria, stranguria, dysuria and/or periuria in the cat.

The cardinal rule of feeding a malnourished or anorectic patient is "use the gut if at all possible."

A review of the classic signs of hyperthyroidism, the best testing strategies and when to use them, and the advantages and disadvantages of surgical and non-surgical therapies.

Over the last several years, there has been a shift in the mineral content of uroliths in cats from predominantly magnesium-ammonium phosphate to calcium oxalate.

Classic signs of anemia include lethargy, weakness, inappetence, pale mucous membranes or icteric membranes if hemolysis is occurring.

Published: December 1st 2011 | Updated:

Published: April 1st 2009 | Updated:

Published: April 1st 2009 | Updated:

Published: April 1st 2009 | Updated:

Published: April 1st 2009 | Updated:

Published: April 1st 2009 | Updated: