
Clinicians working with "exotic species" should establish consistent anesthetic and analgesic protocols to manage cases that require diagnostic or surgical procedures.

Clinicians working with "exotic species" should establish consistent anesthetic and analgesic protocols to manage cases that require diagnostic or surgical procedures.

San Diego - Veterinarians can earn more than 300 CE credits and peruse the offerings of numerous product vendors at the American College of Veterinary Surgeons' Symposium in San Diego Oct. 22-25 at the Manchester Grand Hyatt.

In order to prevent Maggie--a large-breed dog, from licking the wounded area, her owners reversed the Elizabethan collar.
Editor's note: SurgerySTAT is a collaborative column between the American College of Veterinary Surgeons (ACVS) and DVM Newsmagazine. In September, Shawn Mattson, DVM, DVSc, BSc will discuss "Treating Subchondral Bone Cysts in the Fetlock Joint." Dr. Mattson is an ACVS board-certified surgeon who practices at Moore and Company Veterinary Services, a full-service equine hospital in Calgary, Alberta, Canada. Dr. Mattson, previously at the Ontario Veterinary College in Guelph, Ontario, has published scientific articles in the American Journal of Veterinary Research and Veterinary Surgery related to research on orthopedic infections in horses.

While this review will focus on postoperative pain management, it is important that we acknowledge the critical perioperative elements that lay the foundation for ideal patient pain management. Pain control needs to be in place before the surgeon's blade contacts skin in order to minimize central and peripheral sensitization. Without adequate pre-emptive analgesia, the nociceptive process ramps up unabated by general anesthesia. Receptor sensitivity increases and structural rewiring can occur.

The stage was all mine. With trembling hands, I went to work. ... As sheer dumb luck would have it, the surgery went perfectly.

Ligating the ovarian pedicles during an ovariohysterectomy in a large or obese dog can be a challenging task, especially if the ovarian pedicles are thick or surrounded by excessive adipose tissue that is not easily incorporated into simple encircling ligatures.
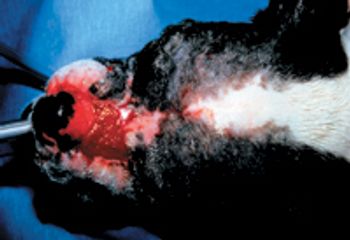
Amputation is a painful procedure, so aggressive, multimodal analgesia is necessary. The patient should receive a premedication that includes a pure mu agonist opioid such as morphine, fentanyl, oxymorphone or hydromorphone.
Three beneficial reconstructive surgery techniques--the adjustable horizontal mattress suture, the mesh skin graft, and punch grafts in pockets--are underused by practitioners. These techniques require no special equipment and are easily accomplished.

We prefer to do surgery in the morning - my favorite time of day - before the telephone starts ringing and emergencies begin showing up. It's peaceful, and surgery usually can be done without hurry or distraction.

When some clients brush off our post-surgery care instructions, they end up paying for it-twice.

To keep the surgical area free of hair when castrating cats, I cut a small diamond-shaped hole in the middle of a green rubber dental dam and place the dam over the surgically prepared testicles.

Should our pregnant associate use a respirator during surgeries to avoid inhaling anesthetic gases?

Cleveland - 5/1/2008 - BrightHeart Veterinary Centers completed an acquisition of Great Lakes Veterinary Specialists (formerly, the Veterinary Referral Clinic), a full-service advanced-care and emergency veterinary hospital in Bedford Heights, Ohio.
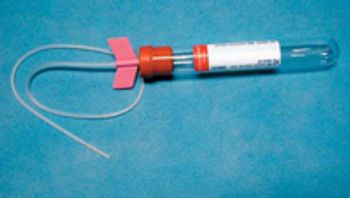
The use of active drains enhances the efficiency and minimizes the morbidity of wound drainage. Their use is indicated for removal of pre-existing fluid, ablation of dead space and prevention of anticipated fluid accumulation.
While interest and controversy swirl around stem-cell use for treating human spinal-chord injuries and diseases ranging from diabetes to Parkinson's, veterinary medicine has been investigating stem-cell use for a variety of animal conditions and diseases.

It is important to recognize qualities that affect candidacy for cataract surgery in our small animal patients.

The term laser stands for light amplification stimulated by emission of radiation.

The Achilles tendon is the common calcaneal tendon and is most commonly injured by laceration in both dogs and cats.

Average healing times for small animal fractures are dependent upon the age of the animal and the type of fracture as well as the method of fixation used to stabilize the fracture.

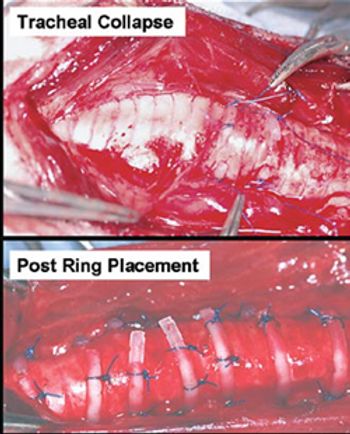
Surgical fenestration of the intervertebral space provides a means of prophylaxis on disc disease.

During this talk, we will be discussing currently available medical and surgical therapies for glaucoma in veterinary medicine, with emphasis on what is new and updated, as well as when their use is appropriate.

Perianal fistula is a specific disease of the canine characterized by ulcerating fistulous tracts, often with a malodorous purulent discharge around the anal orifice.

There have been numerous developments in the field of canine cranial cruciate ligament disease.

The most common indication for total joint replacement in the small animal is osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease that is a cause of significant and frequent pain.