
Mammary gland tumors remain one of the most common cancers in our canine patients.

Mammary gland tumors remain one of the most common cancers in our canine patients.

As the focus of cancer treatments shifts away from conventional chemotherapy to more targeted therapies, a new strategy for the treatment of cancer has become increasingly more popular for both human and veterinary patients.

There is current emphasis in the veterinary field to practice evidence-based medicine. The concept is simplistic, although the practice is not always easy.

Thyroid tumors are relatively uncommon in dogs, accounting for only 1 percent to 4 percent of all tumors. The majority of diagnosed thyroid tumors in dogs are malignant, because adenomas are clinically silent and found incidentally on necropsy.
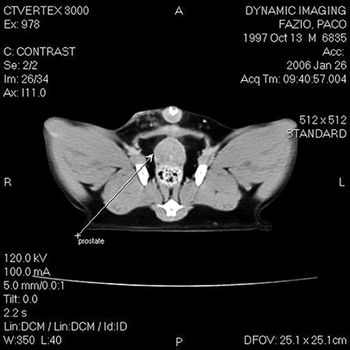
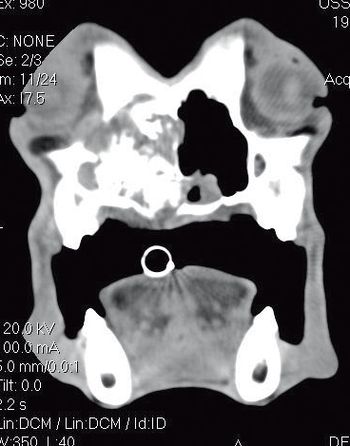
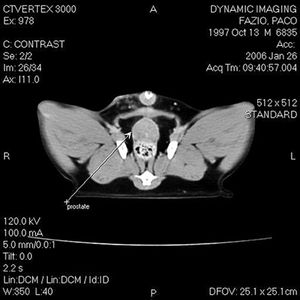
Malignant tumors of the lower urinary tract include transitional cell carcinoma, squamous-cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, leiomyosarcoma, fibrosarcoma, hemangiosarcoma and rhabdomyosarcoma.
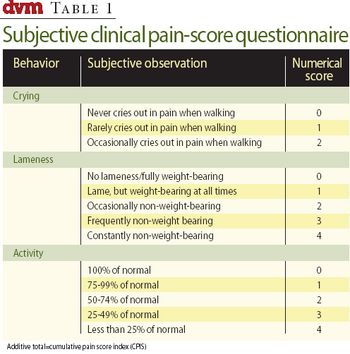
Osteosarcoma is a common cancer to see in larger, middle-aged to older dogs. One of the challenges in treating these patients is pain management. Amputation effectively relieves bone pain and is the standard of care for patients, but may not be an option for all dogs.

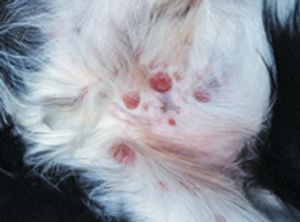
Although anal-sac tumors make up only 2 percent of all cutaneous neoplasms in dogs, they comprise a significant portion of the referrals to veterinary surgeons and oncologists.
Employing different alkylating agents is seen in the design of rescue protocols for lymphoma dogs. oneeded

It is well known that the first attempt at surgery is the one most likely to provide control and/or "cure" of the tumor.

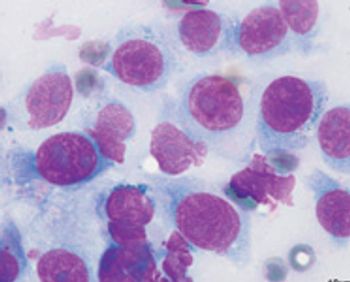
Bone aspirates are becoming increasingly more useful in diagnosis of ... bone lesions. needed
Many clinicians cringe when they see the word histiocytic on a diagnostic report. The nomenclature of histiocytic diseases can be difficult to understand, leading to confusion in regards to diagnostic and therapeutic options. To further compound the confusion, it can be easy to misdiagnose these diseases with only routine histopathology. This article is designed to provide a better understanding of the histiocytic diseases, as well as to provide information regarding the diagnosis and clinical presentation of these diseases and available treatment options.
Author's note: The first article in this series covered melanomas and SCC in dogs (July, DVM Newsmagazine). This article will discuss fibrosarcoma and benign tumors in dogs as well as SCC and fibrosarcoma in cats.
Oral tumors are the fourth most common cancer in dogs and represent 6 percent of all canine cancers. The most common malignant tumors in dogs are melanoma, fibrosarcoma, SCC and osteosarcoma. Benign tumors include the epulides (ossifying, fibromatous and acanthomatous) and other odontogenic tumors. In cats, oral tumors make up 3 percent of all feline cancers. SCC is the most common malignant tumor followed by fibrosarcoma. Benign oral tumors are much less common in cats.

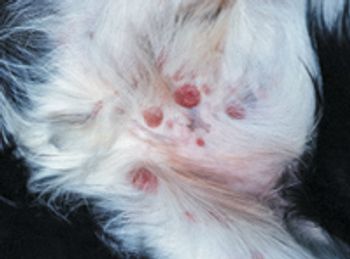
Soft-tissue sarcomas (STS) are common for a practitioner to see as they compromise up to 15 percent of all skin tumors in dogs. The terms spindle-cell tumors and mesenchymal tumors have also been used to describe these tumors. STS are considered to be a family of tumors given that they are all derived from connective tissues and have a similar biologic behavior regardless of the histologic type (see Table 1). Histiocytic sarcomas, oral sarcomas, hemangiosarcoma and synovial cell sarcoma are generally not included given that these tumors have a different biologic behavior.
Published: December 1st 2006 | Updated:

Published: May 1st 2010 | Updated:

Published: January 1st 2010 | Updated:

Published: December 1st 2008 | Updated:

Published: September 1st 2008 | Updated:
Published: July 1st 2008 | Updated: