
A veterinarian explains what to watch for in cats and dogs with bartonellosis.

Bartonellosis is usually transmitted by cat scratches and bites contaminated with flea feces. Learn more about the animals that host and pass on the Bartonella bacteria.

A young mother, athlete, and veterinary practice manager suffered through extreme fatigue and muscle pain for three years before she discovered her life would never be the same. Could the same thing happen to you simply because of where you work?

Veterinary team members, you're at risk for the disease simply because you work with animals. But how much do you really know about bartonellosis?

Bartonella species, their animal hosts, and potential vectors are being identified at a snowballing rate. Learn the risk this poses to you and your patients.

Put your best foot forward -- and shine like the star you are -- at this season's veterinary hospital get-together.

Associations speak out on heartworm preventives. Read what they say about efficacy issues and staying the course.

test

Kansas State University veterinary professors suggest ways to highlight dental health in practice.

In-home blood glucose monitoring can improve prognoses and client compliance at your veterinary practice.

Bargain-basement spays, neuters do more harm to the veterinary profession, than good for animals.

Female dolphins do better when they work with their pod-mates.

Intuitive cooperation doesn't work beyond pairs. It's time to be direct with team members and other coworkers.

Veterinary team members attending CVC San Diego shared the main reason they love going to work every day.

Learn how you can help increase awareness about the prevalence, detection, and treatment of pet cancer.

Your mental health at your veterinary practice may mean doing things differently.

Animals serve many roles when it comes to energy and the planet. Their energy fields are far more expansive than ours – a dog's energy field is approximately ten times that of a human's. A horse's field will encompass a large arena, and a cat's will fill an entire property. The energy of wildlife is especially important to the survival of the planet. They create a frequency that maintains the vibrational health of the planet, and all creatures on it.

Transfusion of blood products is an important lifesaving measure performed frequently in veterinary medicine. The decision to transfuse should not be taken lightly: it is costly and can frequently be clouded by complications. Blood transfusion therapy should be limited to the treatment of anemia, hypoproteinemia, coagulation disorders, or hemodynamic instability.

The role of the veterinary technician in traumatic emergencies is pivotal to the survival of the incoming patient. The physical exam must be quick, thorough, and concise. Utilization of all technical skills from careful visualization, palpation, and auscultation is of the utmost importance.
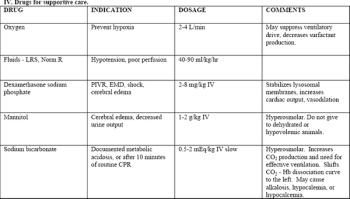
Anesthetic arrests and patients with reversible conditions should be resuscitated aggressively. Reasons for such a poor success rate include severity of underlying disease, delay in the recognition of CPA, and delay in delivery of appropriate therapy.

Energy to most of us is something that turns lights on and off and runs our cars. We don't realize we are made of energy, and that we interact with other humans and animals on an instinctive, energetic basis. Having an awareness of how we affect others allows us to be better colleagues, practitioners and care givers.

As veterinary professionals, we have been trained to create a practice environment that focuses on maintaining cleanliness and reducing disease transmission. While these are vital to the health of our staff and patients, we must also consider other aspects of healing. The emotional and energetic atmosphere our clients, staff and patients are exposed to does influence their physical, mental and behavioral well being. It is our obligation to provide a setting conducive to improving staff work life and patient health.

Capnographs are used to measure ETCO2. Most capnographs use infrared light absorption to measure CO2 levels. Capnographs allow for continuous monitoring of the patients CO2 levels. ETCO2 is reflective of the patients PaCO2 usually within a 5mmHg gradient, this gradient can be affected by pulmonary perfusion.

Idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is defined as gastrointestinal signs (vomiting, anorexia, diarrhea) greater than 3 weeks duration, with incomplete response to dietary trials and anthelmintics, biopsy findings of mucosal inflammation, and clinical response to immunomodulatory therapies.
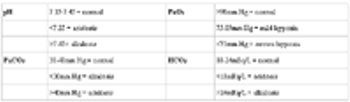
Blood gas analysis provides information about respiratory function and acid/base status. This information is vital in determining and monitoring treatment of patients with primary or secondary respiratory disease and/or metabolic disturbances. Blood gas (BG) can be assessed on arterial (ABG) or venous (VBG) samples, although oxygenation assessment is made on arterial blood only.

In the fasted healthy state glycogen stores are used as the primary energy source. When glycogen stores become depleted, which can occur quickly in strict carnivores such as the cat, amino acids are mobilized from lean muscle.

Veterinarians are faced daily with the therapeutic challenge of treating species and conditions for which no approved drug exists. Other challenges include the differing needs of patients that have species-specific requirements, as well as individual needs for palatability and formulation.

Canine Parvovirus (CPV) is a family of viruses that cause vomiting, hemorrhagic diarrhea, and leukopenia. The virus can infect dogs of any age but, because of effective client education and early, aggressive vaccination protocols, is commonly noted in dogs less than 1 year of age.

Dogs and cats with diabetes can be managed to reduce clinical signs for years after their diabetes diagnosis, but it takes a committed owner to achieve these results.

This handy form helps team members review patient records before appointments.