Aimee C. Kidder, DVM, DACVIM
Articles by Aimee C. Kidder, DVM, DACVIM

Diabetes mellitus (DM) can be defined as a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia, which results from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both. DM can occur because of disease affecting the endocrine pancreas and other endocrinopathies such as acromegaly.

Cats have a different embryological development and anatomy of the pancreas from other species. In cats, unlike other species, the pancreatic duct is the main functional duct; the accessory pancreatic duct usually does not persist. In dogs the pancreatic duct is of minor importance and may be absent.
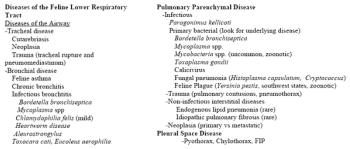
If the cat is presented for labored breathing questions should be directed to assist in differentiating upper from lower respiratory disease as some owners perceive stertorous breathing in a cat with upper respiratory disease as a form of labored breathing. This could be misleading to a clinician.

In the fasted healthy state glycogen stores are used as the primary energy source. When glycogen stores become depleted, which can occur quickly in strict carnivores such as the cat, amino acids are mobilized from lean muscle.

Hepatic lipidosis is the most common liver disease in cats in North America. In a retrospective study performed at the University of Minnesota evaluating liver biopsy specimens obtained from cats over a 10-year period, hepatic lipidosis accounted for 50% of all cases.

The nasal cavity is defined as part of the upper respiratory tract that extends from the nares to the choanae. The choanae is the caudal most part of the nasal cavity that communicates with the nasopharynx.


