
Practitioners provide veterinary care for a growing number of meat goats in the United States - animals known to develop neurological disease.

Practitioners provide veterinary care for a growing number of meat goats in the United States - animals known to develop neurological disease.
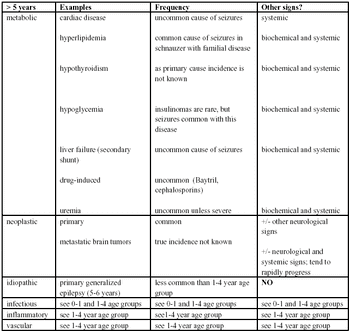
Clients frequently use the term "seizure" to describe many different episodic events.

The primary goal is to treat the underlying disorder.

Animals with acute intervertebral disk extrusion are almost always painful.
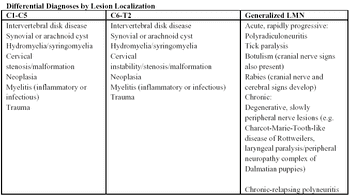
Tetraparesis or tetraplegia is a neurological condition in which all four limbs are weak (paresis) or paralyzed (plegia).

Overview of equine rabies, equine herpes virus-1, and parasitic infection of the CNS

Fibrocartilagenous embolus(i) is an acute spinal cord infarction(s) caused by microscopic spinal vessel occlusion by material histologically resembling the intervertebral disk (nucleus pulposus).
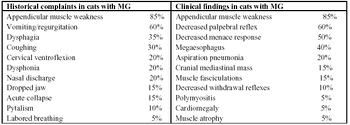
Acquired myasthenia gravis is an immune-mediated disorder in which autoantibodies develop against the neuromuscular junction acetylcholine receptors (AChR).
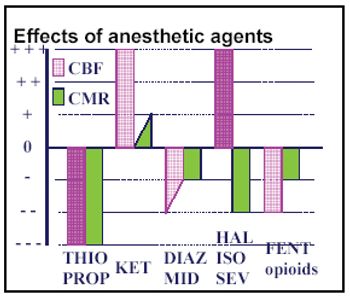
The primary concerns for anesthesia for dogs with spinal neurologic disease are the need to prevent pulmonary aspiration of gastric fluid if food has not been withheld, to maintain a low intracranial pressure (ICP) and therefore a low spinal cord pressure, and the provision for pain management.

Dr. C.W. Dewey gave an excellent lecture at the 2007 American College of Veterinary Internal Medicine Forum on ?Recent and Upcoming Developments with the New Anticonvulsant Drugs.?
A chief concern with any trauma that causes frontal or poll injury is possible damage to the central nervous system.

In four videos, Dr. Joan R. Coates demonstrates how to perform a neurologic exam in a dog.

Part 1 of performing a neurologic examination.

Part 2 of performing a neurologic examination.

Part 3 of performing a neurologic examination.

Part 4 of performing a neurologic examination.

Laser disk ablation, a procedure for preventing thoracolumbar intervertebral disk herniation in dogs, has been developed and performed in more than 350 dogs at the Oklahoma State University Center for Veterinary Health Sciences.

To help reach a prognosis in nonambulatory animals with spinal cord disease, assess voluntary motor function or pain perception.
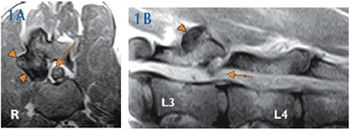
A 6-year-old castrated male Great Dane was presented to the Cornell University Hospital for Animals for evaluation of pelvic limb ataxia and intermittent fecal incontinence.

A 1-year-old 58.3-lb (26.5-kg) castrated male English bulldog presented to the Mathew J. Ryan Veterinary Hospital at the University of Pennsylvania for evaluation of progressive pain that was difficult to localize.
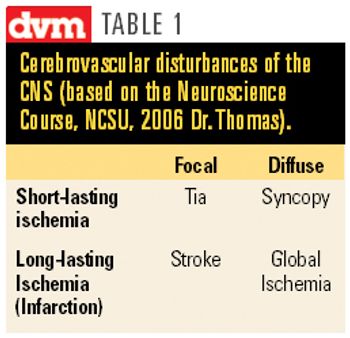
Although brain infarction is the third leading cause of death in humans, cerebrovascular accidents are rarely reported in veterinary literature.

Neurologic diseases are relatively common in companion rabbits and are being identified more frequently because of owners' greater interest in providing better healthcare to their pets, better-trained veterinarians, and improved diagnostic aids.

Two or more seizures without complete recovery of consciousness between seizures, or persistent seizure activity for more than 30 minutes constitute the definition of status epilepticus (SE) in human medicine (Treatment of Convulsive Status Epilepticus. JAMA 1993; 270:854-9).
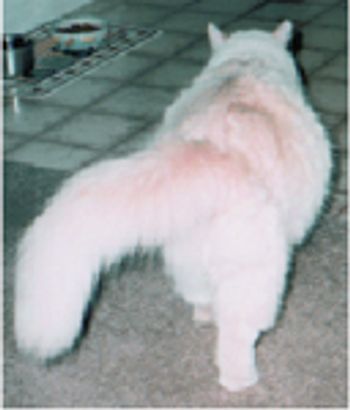
A 10-year-old 8.6-lb (3.9-kg) spayed female domestic medium-haired cat had been evaluated by the referring veterinarian because of lethargy, right pelvic limb lameness, lumbar discomfort, reluctance to jump, and tail weakness.

In Yorkshire Terriers, brainstem involvement has been described.