
In addition to new drug options for refractory canine epilepsy, consider home treatment of cluster seizures to alleviate the need for repeated, costly emergency veterinary care.

In addition to new drug options for refractory canine epilepsy, consider home treatment of cluster seizures to alleviate the need for repeated, costly emergency veterinary care.

Cognitive dysfunction syndrome (CDS) in dogs is thought to be similar to Alzheimer's disease in people. And studies have revealed that people with Alzheimer's disease not only have cognitive deficits, but neurologic deficits as well, such as impaired gait, restlessness, slowness, and, rarely, tremors.
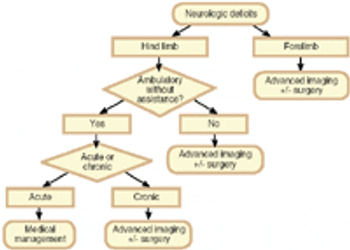
In last month's column we discussed the pathophysiology of intervertebral disk disease (IVDD). Once IVDD is diagnosed, the clinician must again use the history (onset and course of clinical signs) and the physical exam (neurological status) to formulate the therapeutic plan.

This study demonstrates that epileptic dogs treated with phenobarbital alone or in combination with potassium bromide are more likely to be hypertriglyceridemic.

The major goals of therapy for a brain tumor have been to control secondary effects, such as increased intracranial pressure or cerebral edema, and to eradicate the tumor or reduce its size.

Vestibular dysfunction causes varying degrees of loss of equilibrium causing imbalance and ataxia.

The trigeminal nerve is a large nerve that contains both motor and sensory components.

Inflammatory central nervous system diseases are a group of diseases that affect the brain, or brain and spinal cord, in the absence of an (apparent) infectious cause.

Equine infections neurologic diseases are important individual horse disease but can also occur in significant epizootics and outbreaks with substantial economic loss.
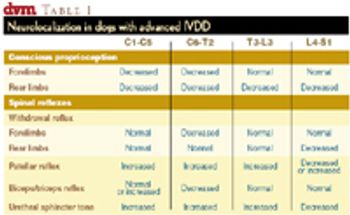
Intervertebral disk disease (IVDD) is one of the most common conditions affecting chondrodystrophic dogs. Signalment, history and thorough neurologic examination are paramount in diagnosing and determining a treatment plan for animals affected with IVDD.

National Report - Pet owners are shopping for price, veterinarians say, and it's impacting general practice and referrals.

Tremors in people are classified/described in many different ways: neuroanatomical location, rate, amplitude, rhythmicity, relationship to rest and movement, posture, performance of specific tasks, medical and family history.
A seizure is the outward manifestation of a paroxysmal cerebral disorder resulting from a transitory disturbance of brain function.

The neurological examination is the most important tool for localizing vestibular signs to either the peripheral or central areas.

If your overall goal of anticonvulsant therapy is to eliminate all seizure activity, there is a good chance you'll fail.

The cavernous sinus is a venous structure that lies on the floor of the skull and encircles the pituitary.

Ventroflexion of neck is not really a specific disease but a clinical sign that has several different etiologies.

Canine Epileptoid Cramping Syndrome (Spike's disease) is a poorly characterized problem in Border Terriers that may be a metabolic, neurological or muscle disorder.

First case: Infraspinatus muscle contracture in the dog
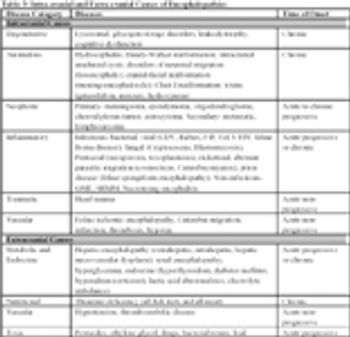
The word encephalopathy literally means "disease or disorder" of the brain.

It is helpful to develop an ordered approach to this problem.
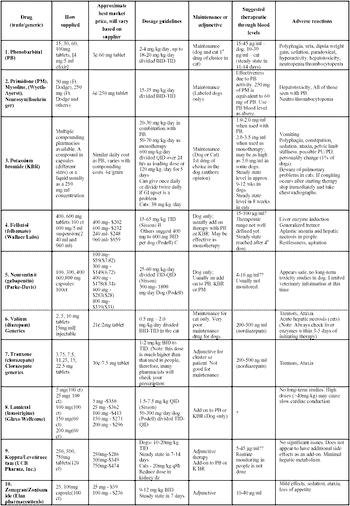
There are varied opinions about this definition but for this discussion we will define a patient as refractory when: 1) an anticonvulsant (AC) has been used as monotherapy, the high end of the "therapeutic" blood level has been achieved for the AC and the patient continues to have the same or an increased number of seizures (szs); 2) a patient that has developed side effects from an AC that now precludes its use; or 3) the patient that has been well controlled for months or years and recently has had a significant increase in sz frequency.

In the field of equine neurology, there has been the discovery of a few new disorders, in addition to some newer diagnostics, and/or therapeutics.

Disease processes are categorized into Congenital, Degenerative, Developmental, Inflammatory, Metabolic, Neoplastic, Traumatic and Miscellaneous processes.

Case 1: Herd of 150 Angus crossbred cows, gave birth to these calves.