
Dr. David S. Bruyette describes how to handle cats in this situation.

Dr. David S. Bruyette describes how to handle cats in this situation.

Denver -- The Morris Animal Foundation (MAF), in an effort to increase veterinary research into feline health issues, has launched the Happy Healthy Cat Campaign.

CATalyst's Dr. Jane Brunt offers tips on how to treat cats well-and draw more of their owners in the door.

Osteoarthritis may be categorized as primary or secondary.

As in dogs, obesity may contribute to osteoarthritis or the clinical manifestations of osteoarthritis in cats.

Osteoarthritis treatment falls into three categories: lifestyle changes, pharmacological intervention, and nonpharmacological intervention.

Although the terms degenerative joint disease and osteoarthritis are commonly used interchangeably in the veterinary arena, a distinction has been made between the two.

Compared with the radiographic features of feline osteoarthritis, the clinical signs of feline osteoarthritis are not well-documented.

It appears to be more common than previously thought and could be a major cause of discomfort in senior cats.

Dr. Sheilah Robertson explains how to use this drug in cats with osteoarthritis.

Dr. Sheilah Robertson discusses what cat owners can do to help their cats with chronic pain.

Franklin, Tenn. -- Mars Petcare US voluntarily recalled a limited number of bags of SPECIAL KiTTY® Gourmet Blend dry cat food sold at Wal-Mart stores in 15 states, following a positive test result indicating potential Salmonella contamination.
What is a cat? What characteristics are different for this species than we are or dogs are?

Dramatic changes have occurred in the past 10 years regarding the way veterinarians view vaccines and vaccination practices.

Feline calicivirus (FCV) is best known for its role in causing acute upper respiratory disease and oral ulceration in kittens and cats.

Disease of the oral cavity is a common problem, particularly in middle-aged to older cats.

The chronic feline snuffler is a frustrating patient to treat.

Renal insufficiency/failure is the most common cause of morbidity and mortality in older cats.

Feline Infectious Peritonitis (FIP) represents the worst outcome of infection with a common group of viruses: the feline coronaviruses (FCoVs).

Constipation is defined as the infrequent or difficult evacuation of stool.
Obesity is the number one nutritional disorder in pets in the western world. Twenty five percent of cats seen by veterinarians in the USA and Canada are overweight or obese.
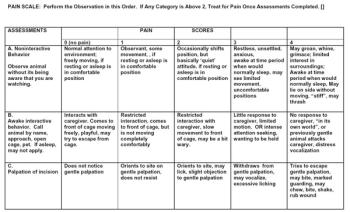
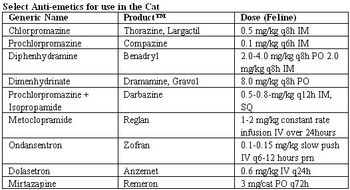
Cats are notorious for concealing pain. In contrast to dogs, they rarely vocalize in response to ain unless pushed to the limit.

Bartonella henselae is the primary etiologic agent in Cat Scratch Disease, which causes fever and lymphadenopathy in humans.

Vaccination has generally been considered to be a benign procedure in veterinary medicine. Unfortunately, soft tissue sarcoma development subsequent to vaccination (vaccine-associated sarcoma) in cats has dramatically changed this view within our profession over the last twenty years.

Head and neck tumors are relatively common in cats. An understanding of the differentials in this anatomic location is very important as the diagnostic and therapeutic approach may vary.