
Philip Bergman, DVM, PhD, MS, DACVIM (Oncology), discusses some of the latest advances in veterinary oncology
Dr. Philip Bergman, DACVIM, is a medical director for the online cancer management program called Oncura.

Philip Bergman, DVM, PhD, MS, DACVIM (Oncology), discusses some of the latest advances in veterinary oncology

Philip Bergman, DVM, PhD, MS, DACVIM (Oncology), discusses his lecture “Mast Cell Tumors: The Latest and Greatest,” in an interview with dvm360

Philip Bergman, DVM, PhD, MS, DACVIM (Oncology), talks about his lecture “Lymphoma – What’s New?”, presented at the Fetch dvm360 conference in Atlantic City, New Jersey

Philip Bergman, DVM, PhD, MS, DACVIM (Oncology), talks about compounded CCNU, as well as the precision of 503B outsourcing facilities

Paraneoplastic syndromes (PNS) are neoplasm-associated alterations in bodily structure and/or function that occur distant to the tumor. They are an extremely diverse group of clinical aberrations that are associated with the non-invasive actions of the tumor.

Paraneoplastic syndromes (PNS) are neoplasm-associated alterations in bodily structure and/or function that occur distant to the tumor. They are an extremely diverse group of clinical aberrations that are associated with the non-invasive actions of the tumor.

Mammary gland tumors (MGT) are some of the most common tumors seen in veterinary clinical practice. They are the most common tumor seen in the female dog and the second most common tumor of the female cat.
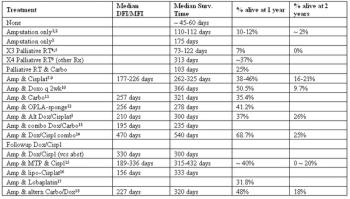
Osteosarcoma (OSA) is the most common primary bone tumor in the dog (85% of skeletal malignancies). It is estimated to occur in over 8,000 dogs/year in the United States.

Head and neck tumors are relatively common in cats. An understanding of the differentials in this anatomic location is very important as the diagnostic and therapeutic approach may vary.

Lymphoma (LSA) is the most common tumor of the cat and represents approximately 80-90% of hematopoietic tumors in cats. LSA is the third most common tumor in the dog with an estimated annual incidence of 13-24/100,000 dogs at risk.

Mast cell tumors (MCT's) are the most common tumor in the dog and the second most common tumor in the cat. MCT's are primarily a disease of older dogs and cats, however, extremely young dogs and cats have been reported to have MCT's.

Vaccination has generally been considered to be a benign procedure in veterinary medicine. Unfortunately, soft tissue sarcoma development subsequent to vaccination (vaccine-associated sarcoma; VAS) in cats has dramatically changed this view within our profession over the last twenty years.

Canine malignant melanoma (CMM) of the oral cavity, nail bed, foot pad and mucocutaneous junction is a spontaneously occurring, highly aggressive and frequently metastatic neoplasm. CMM is a relatively common diagnosis representing ~ 4% of all canine tumors and it is the most common oral tumor in the dog.
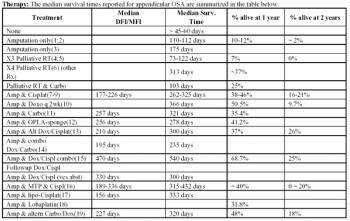
Osteosarcoma is the most common primary bone tumor in the dog (85% of skeletal malignancies). It is estimated to occur in over 8,000 dogs/year in the United States.

Canine malignant melanoma of the oral cavity, nail bed, foot pad and mucocutaneous junction is a spontaneously occurring, highly aggressive and frequently metastatic neoplasm.

Lymphoma (LSA) is the most common tumor of the cat and represents approximately 80-90% of hematopoietic tumors in cats. LSA is the third most common tumor in the dog with an estimated annual incidence of 13-24/100,000 dogs at risk.

Vaccination has generally been considered to be a benign procedure in veterinary medicine. Unfortunately, soft tissue sarcoma development subsequent to vaccination (vaccine-associated sarcoma) in cats has dramatically changed this view within our profession over the last twenty years.

Head and neck tumors are relatively common in cats. An understanding of the differentials in this anatomic location is very important as the diagnostic and therapeutic approach may vary.

This discussion will review what I feel to be the top 10 clinically relevant advances in veterinary oncology over the last approximately 10 years.

Mammary gland tumors are some of the most common tumors seen in veterinary clinical practice.
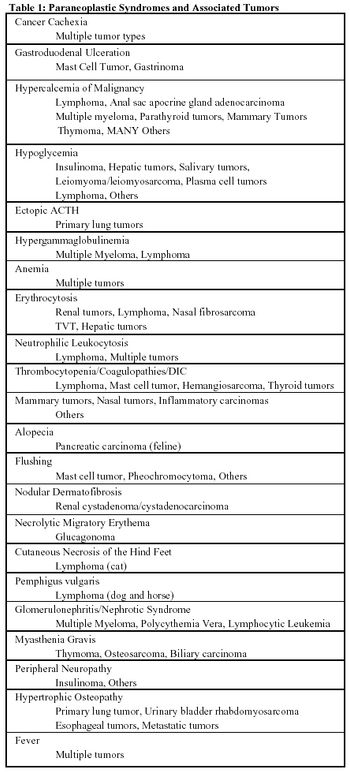
Paraneoplastic syndromes are neoplasm-associated alterations in bodily structure and/or function that occur distant to the tumor.

Mast cell tumors are the most common tumor in the dog and the second most common tumor in the cat.

Published: November 26th 2024 | Updated:

Published: November 27th 2024 | Updated:

Published: November 20th 2024 | Updated:

Published: November 22nd 2024 | Updated:

Published: August 1st 2010 | Updated:

Published: August 1st 2010 | Updated: