
There has been much published on gastric ulceration in horses in the last 10 years. In this hour we will discuss the diagnostics, risk factors and treatment of gastric ulcers. We will concentrate on current, clinically applicable information.

There has been much published on gastric ulceration in horses in the last 10 years. In this hour we will discuss the diagnostics, risk factors and treatment of gastric ulcers. We will concentrate on current, clinically applicable information.

In horses with primary cecal impactions, there is a gradual onset of abdominal pain similar to the development of a large colon impaction. The typical time course is 5-7-days. During this time, veterinarians may use treatments for impactions, such as intravenous administration of analgesics and nasogastric administration of laxatives such as mineral oil, dioctyl sodium sulfocuccinae (DSS) or magnesium sulphate (Epsom salts).

Although there has been a substantial increase in our understanding of postoperative complications in recent years, the treatments remain very much the same. For ileus, these treatments include decompression of the stomach, replacement of fluid and electrolyte losses with parenteral fluids, and use of a variety of prokinetic agents. For adhesions, treatments include anti-inflammatory medications and antibiotics, although some of the newer physical agents such as carboxymethylcellulose offer new modalities for combating this problem.
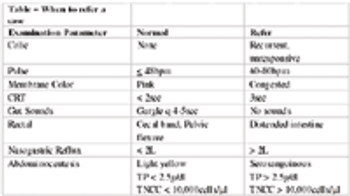
Triaging colic patients.

Pneumonia caused by Rhodococcus equi continues to be an important cause of disease and death in foals.1 Because case-fatality rates may be high and because treatment may be prolonged and expensive, controlling and preventing disease is more desirable than relying solely on treating affected cases.

The palmar digital nerves are blocked by injecting up to 2 ml of anesthetic over the nerves, along the edge of the DDFT. Much discussion has taken place regarding the proximal to distal level that the injection should occur. The PDN can be blocked anywhere from the proximal margin of the collateral cartilage to the mid pastern region.

A new study in top equine athletes brings nutritional deficiencies into the spotlight.

Could this common fracture eventually be a thing of the past?

Stay safe with these restraint tips for working around ill or injured horses.

The coordinated actions of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems result in the transport of oxygen and energy products (glucose, fatty acids) to the muscle fibers, where they are used for aerobic energy production, and the removal of waste products (lactate, carbon dioxide, water) from them.

The cornea is the front layer of the fibrous tunic of the eye; it is composed of three distinct layers and one distinct membrane. The outer epithelial layer is approximately five to ten cells thick. The middle stromal layer comprises about 95% of the cornea, and the inside layer is the endothelial layer, and its basement membrane is Descemet's membrane.
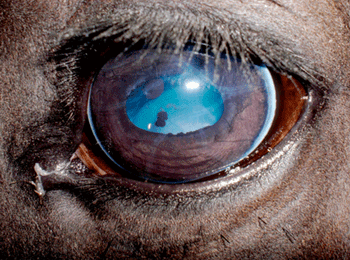
What condition are these ocular changes consistent with?
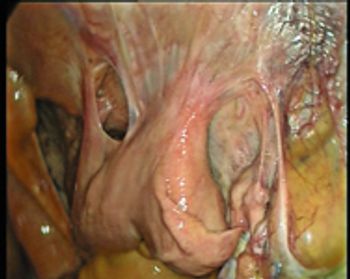
Uteropexy can help mares that develop post-mating endometritis.

A look at how several antifungal agents and delivery vehicles affect equine keratocytes.

A plan eight years in development will finally come to fruition.

Each of these promising veterinary students attributes a personal passion for equine medicine to an early association with horses.
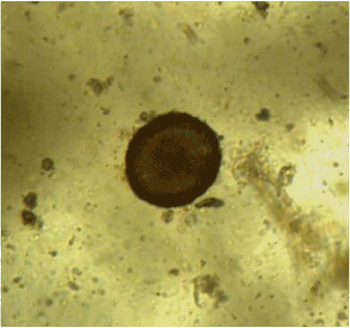
Which parasite is bugging this colt?

The use of a modified spirometric monitoring system for anesthetized equine patients was recently evaluated.

Get the veterinary lowdown on five plants toxic to horses, where they're found, and the consequences of a horse ingesting them.

Often clients will consult their veterinarians regarding conditioning, nutrition, supplementation and managing horses exercising in extreme heat.

For those pursuing equine practice, the personal passion for their subjects starts long before veterinary school.
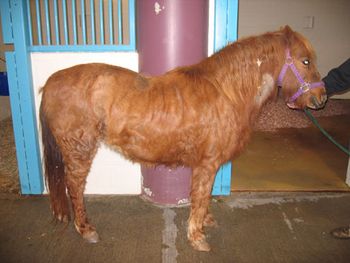
Which diagnostic test will solidify a diagnosis for this pony?

North Carolina State University's College of Veterinary Medicine recently published a retrospective study looking at the demographics of horses donated to their Equine Health Center from 1996 to 2008.

Corneal disease and damage resulting in cloudy, blue eyes has many causes.

Bacterial pneumonia is a common cause of disease in young foals.