
Davis, Calif. -- A team of researchers at the University of California, Davis, School of Veterinary Medicine say a gene mutation is responsible for high levels of uric acid, and sometimes bladder stones, in Dalmatians.

Davis, Calif. -- A team of researchers at the University of California, Davis, School of Veterinary Medicine say a gene mutation is responsible for high levels of uric acid, and sometimes bladder stones, in Dalmatians.
During the past three decades, a tremendous amount of information has been generated regarding the etiology, detection, treatment, and prevention of canine urolithiasis.

Many forms of glomerular disease are thought to be associated with the presence of immune complexes in glomerular capillary walls.

Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a common problem that affects an estimated 0.5 to 7% of dogs and 1.6 to 20% of cats.

Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a common problem that affects an estimated 0.5 to 7% of dogs. Radiographic signs of osteoarthritis (OA) occur in 20% of dogs.

Acute kidney injury often results from ischemic or toxic insults and usually affects the most metabolically active tubular portions of the nephron.
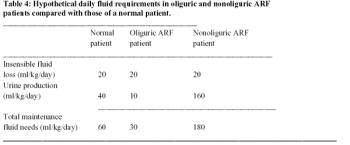
Clinical signs associated with prerenal azotemia are often nonspecific and may be similar to those caused by ARF.

The urinalysis (UA) is an often overlooked and underutilized test in veterinary medicine.

Most bacterial infections of the lower urinary tract respond quickly to antimicrobial treatment; however, urinary tract infections (UTI) associated with defects in the host immune system (complicated UTI) often fail to respond or recur after antibiotic withdrawal and can be a therapeutic challenge.

By altering pre-glomerular resistance, healthy kidneys can maintain relatively stable glomerular capillary pressures despite variations in systemic blood pressure.

Renal damage and disease can be caused by acute or chronic insults to the kidney.

FLUTD refers to a spectrum of diseases that result in pollakiuria, hematuria, stranguria, dysuria and/or periuria in the cat.

Over the last several years, there has been a shift in the mineral content of uroliths in cats from predominantly magnesium-ammonium phosphate to calcium oxalate.
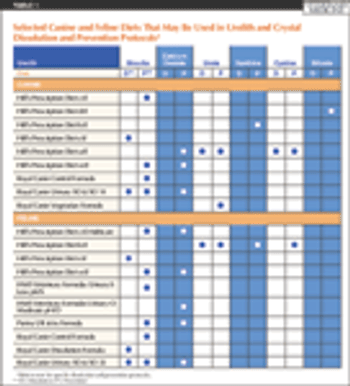
Urolithiasis is common in dogs and cats, causing morbidity and, occasionally, mortality.

Give this form to clients with overweight cats to help them understand the ins and outs of weight loss.
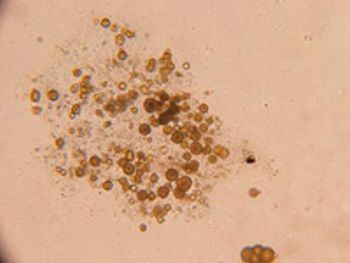
What is your interpretation and diagnosis?
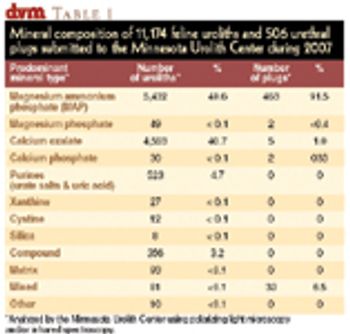
In 1981, calcium oxalate was detected in only 2 percent of feline uroliths submitted to the Minnesota Urolith Center, whereas struvite was detected in 78 percent. However, beginning in the mid-1980s, a dramatic increase in the frequency of calcium oxalate uroliths occurred in association with a decrease in the frequency of struvite uroliths (Figure 1) .
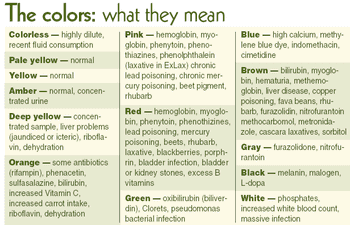
In the Dr. Seuss classic Go Dogs Go, we learn a very important lesson that remains with us throughout our lives: Red means stop.
Malignant tumors of the lower urinary tract include transitional cell carcinoma, squamous-cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, leiomyosarcoma, fibrosarcoma, hemangiosarcoma and rhabdomyosarcoma.


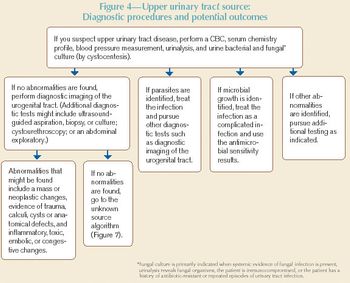
This article and the accompanying algorithms are intended to guide practitioners through the series of steps necessary to confirm the presence of hematuria, localize the source of the RBCs, and identify the specific cause.

Urinary incontinence is a common problem that is very vexing to clients, and frequently to veterinarians.

Intrinsic renal failure occurs when damage to the renal parenchyma occurs.
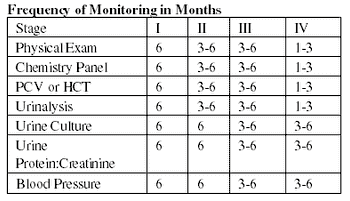
The International Renal Interest Society (IRIS) has developed a system to stage chronic kidney disease (CKD).