Since ultrasonography is becoming more accessible to all veterinary practitioners, learn all about this ultrasonographic examination protocol for trauma and start saving lives.

Since ultrasonography is becoming more accessible to all veterinary practitioners, learn all about this ultrasonographic examination protocol for trauma and start saving lives.
If you have access to this advanced imaging technology, use it to its full advantage by having it to guide you to exactly what you want to sample.

Veterinary radiologist Dr. Wm Tod Drost answers questions from CVC attendees about using ultrasonography to collect fine-needle aspirates and biopsy samples.
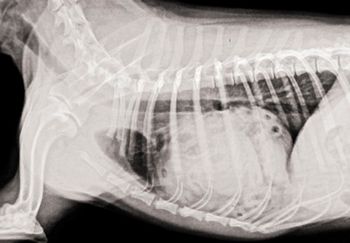
A hernia repair leads to this unusual radiographic finding.

Respiratory tract disease is both serious and extremely common

Coughing Dog with a Murmur: Now What?
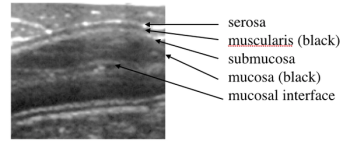
In the dark ages of ultrasound, small intestinal loops were merely black rings on the ultrasound screen.

The goals of this lecture are to provide you with techniques of radiography and radiology of the dog and cat thorax

The normal vascular flow to the liver is dual with a larger portion coming portal vein (80%) than the hepatic arteries (remaining 20%).

The most important question to ask yourself is: Is the lung too opaque or too lucent?

Learning ultrasound is hard enough! Haven't we done enough just to make accurate descriptions and list most appropriate differential diagnoses?

The inherent poor contrast within the abdomen and the fact that soft tissue and fluid can not be differentiated radiographically means that contrast media are required for assessment of luminal surfaces, and therefore wall thicknesses of the gastrointestinal tract.

Looking to make an investment for your practice this year? Put a digital dental radiography unit on your wish list, and you and your patients will all have happy and healthy smiles.

Hear how digital radiography systems can optimize the dental radiographs you capture.

Equine arthroscopy is commonly used to manage problems in carpal joints, hocks and stifles. But what about managing a tear in a flexor tendon or navicular bursa? Get your moneys worth out of this instrumentand provide optimal patient careby giving some less conventional uses a try.
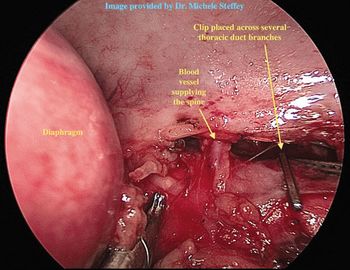
New technology may become protocol of choice at veterinary teaching hospitals.

A look at some pointers for evaluating a cat for heart disease.In "Feline cardiology: A review of the basics," Jan Bright, DVM, MS, DACVIM (internal medicine, cardiology), discussed some of the peculiarities of feline cardiology and offered tips to keep in mind when evaluating feline patients with suspected heart disease.

Dr. Ryan King provides a brief overview of which cases are best suited for CT vs. MRI.From the CVC in San Diego, veterinary radiologist Dr. Ryan King provides a brief overview of which cases are best suited for computed tomography (CT) vs. magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).

Dr. Ryan King outlines which forms of imaging are most helpful in certain clinical cases.


A contrast enema study helped clinicians detect an intestinal stricture in this exotic pet. See how this diagnostic step can help your reptile patients with similar signs.
Be sure to look a little deeper when using this technique during your search for a ruptured bladder to prevent missing the diagnosis.
What lies beneath this little dog's bite wounds?

Check out the stories, photos and floor plans of these 10 Merit Award-winning veterinary hospitals.