
One of the most important assessments a veterinarian can make is whether or not oxygen delivery is adequate. Unfortunately, it is not possible to easily or directly assess oxygen delivery in our patients.

One of the most important assessments a veterinarian can make is whether or not oxygen delivery is adequate. Unfortunately, it is not possible to easily or directly assess oxygen delivery in our patients.

Anesthetic mishaps can lead to patient morbidity and mortality. Most problems anesthesia-related problems can be prevented by advanced planning, training, patient monitoring, and the development of standard operating protocols.

Patients are typically sedated or anesthetized and placed in sternal or lateral recumbency. Next, the cranial edge of the wings of the ilia are palpated. Once located, a 10 cm by 10 cm area of hair directly over the lumbosacral junction is clipped and the skin is surgically prepared.

The purpose of this presentation is to review several articles published in veterinary journals over the last three years and to present them in a way that is relevant to the practicing veterinarian.

Details on a recently published a set of guidelines for the long-term use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in cats.

Cesarean section may be indicated for animals with prolonged gestation periods, refractory uterine inertia (primary or secondary), or those with obstructive dystocias. In addition, elective cesarean section may be done in those breeds with consistent fetal oversize (i.e., English bulldogs).

The field of invertebrate medicine is in its infancy. Traditionally veterinary interest in invertebrates has centered on the control of species that are involved in vertebrate disease processes. The husbandry and medical care of captive invertebrates has typically fallen to scientists and hobbyists, with very little veterinary involvement. Now, as many institutions and private individuals maintain large invertebrate collections, a genuine interest exists in advancing the quality of medical care available for these taxa.

What should electronic anesthetic monitoring systems check for?

All veterinary team members play a role in providing patients safe anethetic experiences.

Anesthesia is a vital inclusion in any clinic's medical practice, but it does come with risks. By avoiding these common mistakes, your patients will receive a safer anesthetic experience.

A Q&A with Dr. James Gaynor.

Don't assume dental procedures are of little anesthetic risk.

The results of a University of Wisconsin randomized controlled trial assessing the efficacy of retrobulbar analgesia on the control of postoperative pain in dogs undergoing enucleation was recently published.

A common source of chronic pain in pets.

The use of a modified spirometric monitoring system for anesthetized equine patients was recently evaluated.

When assisting with anesthesia and surgery, our technician sets her cell phone, which is in her pocket, to vibrate every five minutes.

Kansas City -- Of all the regulatory issues veterinarians face, the use and storage of controlled substances can be the most contentious.

Another possible cause of abnormal capnograph readings.

A recent study looked at the effects of gabapentin for use as adjunctive perioperative pain control in dogs.

We already know that the way we each perceive pain will be different depending on our past experiences. The way we respond to that pain also varies from person to person. These two points make recognizing and treating pain difficult, especially in regards to our veterinary patients.
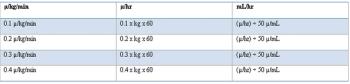
There are a wide variety of pain management techniques. I hope to cover a few here. Some of the different areas we will cover are injectable analgesia, epidurals, wound soaker catheters, local blocks, NSAIDs, and alternative methods. Each group will be expanded upon, with specific examples.

The biggest concern with all exotic animals under anesthesia is hypothermia. Other main concerns include airway access, intravenous access, pain management, and hemorrhage.

Due to the fact that critical patients are more fragile than stabile patients, they require special nursing care. The same is true of these special patients under anesthesia.

Veterinary technicians are the veterinary hospital's mainstay when it comes to carefully and successfully anesthetizing critical patients. A large number of elderly canine and feline patients are affected by cardiac disease, and knowledge of how to safely monitor, anesthetize, and problem solve cardiac patients makes for a less stressful anesthesia for both the patient and technician.

Monitoring, for these purposes will consist of checking vitals on a regular basis. The vitals being monitored may be changed based upon the patient's status and the procedure performed. By watching for changes in trends we are able to catch and potentially stop a crisis from happening..