An introduction to the principles of clinical blood gas analysis and interpretation--including two case examples.
Veterinary Specialist Services
P.O. Box 504
Conifer, CO 80433

An introduction to the principles of clinical blood gas analysis and interpretation--including two case examples.
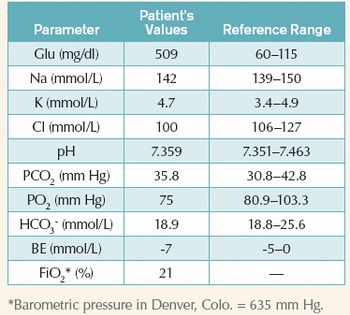
An 8-year-old 44-lb (20-kg) spayed female Siberian husky is a poorly regulated diabetic presenting for surgical excision of a grade I fibrosarcoma on the right thoracic wall.

A 5-year-old 37.6-lb (17.1-kg) neutered male border collie has a three-day history of vomiting.

Patient stress is probably a contributing factor in some cases of adverse patient outcome. Stress during induction of anesthesia can increase circulating catecholamine concentration predisposing the heart to arrhythmias.

A continuous rate infusion (CRI) is a dosing regimen used to deliver a constant amount of drug per unit time. The most common CRIs are administered intravenously; however, other methods such as transdermal deliver mimic the characteristics of CRIs.

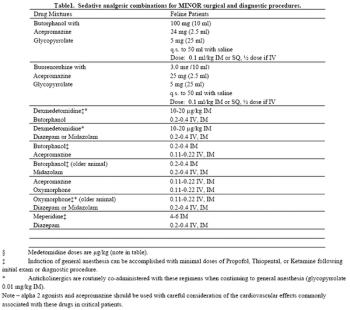
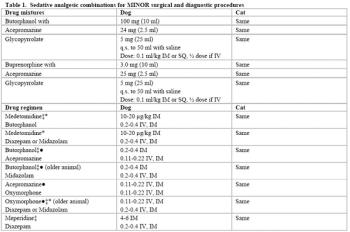
Alpha 2 adrenergic agonists bind to alpha 2 receptors located in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord and brainstem, modulating the release of substance P, calcitonin gene-related peptide and various other neurotransmitters involved in rostral transmission of nociceptive information.

Accurate measurement of pain perception in individual non-human patients is impossible. However, management of pain requires objective measures of effectiveness of the applied treatment.

Use of analgesics prior to surgery (preemptive analgesia) may also be beneficial. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are commonly being administered during the perioperative period. Debate exists as to when to administer the drugs (preoperatively vs. postoperatively).
Anesthetic and pain related mortality would appear to be an easily quantifiable statistic that could be used to measure the outcome of the profession's current anesthetic practices. However, to rely solely on death rate as the measure of the quality of anesthetic care provided is inadequate. The anesthetist's goal should be to minimize the risks to the patient's health while reducing pain and stress.

Patients are typically sedated or anesthetized and placed in sternal or lateral recumbency. Next, the cranial edge of the wings of the ilia are palpated. Once located, a 10 cm by 10 cm area of hair directly over the lumbosacral junction is clipped and the skin is surgically prepared.

Patients vary and accidents occur. This truth emphasizes the need for patient monitoring. One only need visit the exhibit hall of a major veterinary meeting to appreciate the advancements made in veterinary patient monitoring.

Anesthetic related mortality would appear to be an easily quantifiable statistic that could be used to measure the outcome of the profession's current anesthetic practices. However, to rely solely on death rate as the measure of the quality of anesthetic care provided is inadequate.

Patients are typically sedated or anesthetized and placed in sternal or lateral recumbency. Next, the cranial edge of the wings of the ilia are palpated.

Pulse oximeters are relatively inexpensive and provide continuous information about pulse rate and hemoglobin saturation. Pulse oximetry has limitations that need to be understood by the anesthetist.

Accurate measurement of pain perception in individual non-human patients is impossible. However, management of pain requires objective measures of effectiveness of the applied treatment.
Patient stress is probably a contributing factor in some cases of adverse patient outcome. Stress during induction of anesthesia can increase circulating catecholamine concentration predisposing the heart to arrhythmias.

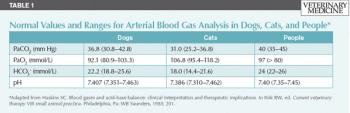
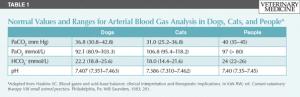
In the past blood gas analysis and interpretation was performed primarily at university and large referral hospitals. The main argument against not using blood gas analysis to guide case management in private practice was the cost of purchasing and maintaining a bench-top blood gas analyzer. With the availability of relatively inexpensive point of care units such as the i-STAT and IRMA, blood gas analysis and interpretation has become more common.

The electrocardiogram is a useful monitoring tool, but its proper use requires training. It provides a heart rate and a picture of the electrical activity of the heart muscle. The anesthetist should be trained to recognize many commonly encountered intraoperative arrhythmias (e.g., multifocal and unifocal ventricular premature complexes, atrioventricular blockade, ventricular tachycardia, etc.) and the veterinarian should be prepared to treat arrhythmias when they occur (if necessary).
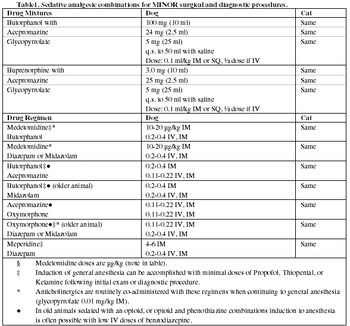
Anesthetic and pain related mortality would appear to be an easily quantifiable statistic that could be used to measure the outcome of the profession's current anesthetic practices. However, to rely solely on death rate as the measure of the quality of anesthetic care provided is inadequate.

Alpha 2 adrenergic agonists bind to alpha 2 receptors located in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord and brainstem, modulating the release of substance P, calcitonin gene-related peptide and various other neurotransmitters involved in rostral transmission of nociceptive information.

Pulse oximeters are relatively inexpensive and provide continuous information about pulse rate and hemoglobin saturation.

Anesthetic related mortality would appear to be an easily quantifiable statistic that could be used to measure the outcome of the profession's current anesthetic practices.

Alpha 2 adrenergic agonists bind to alpha 2 receptors located in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord and brainstem, modulating the release of substance P, calcitonin gene-related peptide and various other neurotransmitters involved in rostral transmission of nociceptive information.

The emphasis on providing humane care and good pain management to small animal patients has primarily focused on dogs, and the pharmaceutical products available for use in that species.
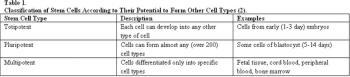
The emerging field of Regenerative Medicine has many definitions; however the NIH's definition, "A treatment in which stem cells are induced to differentiate into the specific cell type required to repair damaged or destroyed cell populations or tissues" provides a basis for further discussion of stem cell therapies and their role in daily practice.

In the past blood gas analysis and interpretation was performed primarily at university and large referral hospitals.

The electrocardiogram is a useful monitoring tool, but its proper use requires training.

Patients vary and accidents occur. This truth emphasizes the need for patient monitoring.
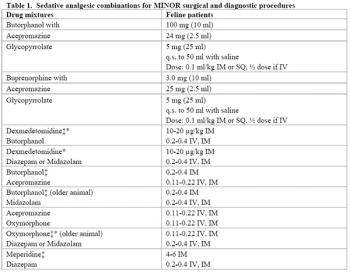
Premedication with a tranquilizer or sedative will help reduce anxiety and stress during the perioperative period.
Published: November 1st 2010 | Updated:
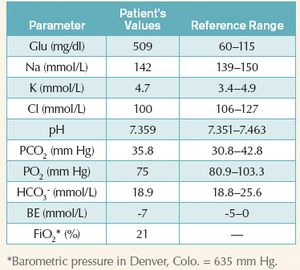
Published: November 1st 2010 | Updated:
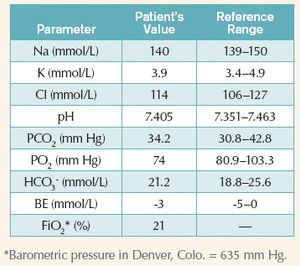
Published: November 1st 2010 | Updated:

Published: November 1st 2010 | Updated:

Published: November 1st 2010 | Updated:

Published: November 1st 2010 | Updated: