
Which agents are good choices for use in regional nerve blocks?

Which agents are good choices for use in regional nerve blocks?

Because we want to succeed! If we want to do the best medicine possible and give our patients the best chance to heal, then we have to treat pain. Pain initiates a fairly profound stress response and a sympathetic overdrive. Stress and autonomic imbalance are not benign and the cascade of side effects include gastrointestinal (GI) ileus, GI ulceration, clotting dysfunction, hypertension, tachycardia, tachyarrhythmias, and many others.

Acute pain has an initial biological purpose in that it initiates a protective withdrawal reflex when a painful stimulus is encountered so that the tissue damage is minimized. Because of its usefulness, acute pain is often called 'physiologic pain'. Unfortunately, unlike acute pain, chronic pain serves no biological purpose.

No matter what anesthetic protocol is chosen, the addition of adequate analgesia is imperative for safe anesthesia. Most anesthetic agents, including the anesthetic gases, block the brain's response to pain but don't actually block pain. If the pain is severe enough, the brain can still respond and make the animal appear to be inadequately anesthetized.

Local anesthetic drugs are extremely effective, inexpensive and easy to use. When local anesthetic drugs are administered, pain impulses originating in the periphery are blocked and prevented from reaching the central nervous system.

The framework of effective pain management systems rests solidly on the foundation of recognition/assessment, pre-emption, and using multiple modalities. Multiple modalities allow for intervention at several different places of the nociceptive pathway, increasing effectiveness and minimizing the need for high or protracted doses of any one particular drug.
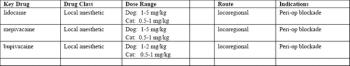
Local anesthetics were once a mainstay of pain management in veterinary medicine, and may now be one of the most under-utilized modalities. Administered locally or regionally, they are the only modality that renders complete anesthesia to a site, i.e. no transmission of nociceptive impulses as long as the drug exerts its effect.

Our patient population has changed fairly dramatically in the last 10 years as our medical skills have progressed and we have become capable of supporting patients with advanced disease and advancing age. With this new set of patients comes a new set of problems, like chronic pain.

It is now a settled matter that the adaptive capacities of animals, coupled with the innate biases of human observers, seriously impairs our ability to "know" which of our patients are in pain, how much they are in pain, and sometimes, even where they are in pain. Historically the absence of behaviors easily associated with pain (crying, whimpering, etc.) has been equated with the absence of pain.

The framework of effective pain management systems rests solidly on the foundation of recognition/assessment, pre-emption, and using multiple modalities. Multiple modalities allow for intervention at several different places of the nociceptive pathway, increasing effectiveness and minimizing the need for high or protracted doses of any one particular drug.

Synthetic opioids are powerful, useful tools to manage pain for one simple reason: Receptors for naturally-occurring opioids (endorphins, enkephalins) are distributed ubiquitously throughout the body and can be found in both central and peripheral tissues.

Our patient population has changed fairly dramatically in the last 10 years as our medical skills have progressed and we have become capable of supporting patients with advanced disease and advancing age.

Good analgesic effect for patients with osteosaroma, especially those with metastatic diesease. Biphosphonates inhibit osteoclastic activitiy, thereby reducing bone resorption and they promote repair through stimulation of osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. They have poor oral absorption so are given by the IV route.

You can never become good at pain management without understanding basic pain pathways. You will have trouble understanding pain pathways without understanding the terminology used to describe them.
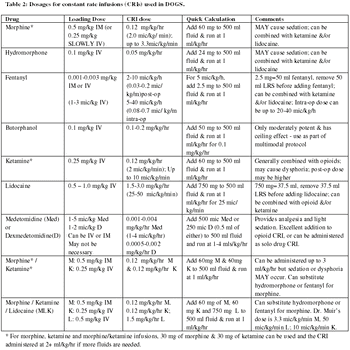
Constant rate infusions (CRI) of analgesic drugs are an excellent way to manage pain in both dogs and cats.
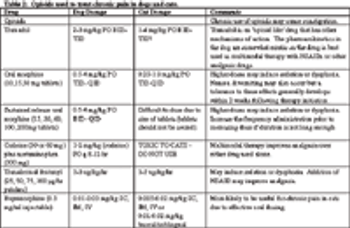
Opioids are a group of natural derivatives or synthetic relatives of opium, which is extracted from the exudate of seedpods of the opium poppy, Papaver somniferum. The poppy plant appears to have been cultivated in ancient civilizations, like those of Persia, Egypt and Mesopotamia, and the first known written reference to the poppy appears in 4,000 BC (from 'A Brief History of Opium' at http://opiates.net).

The endocrine systems throughout the body play crucial rolls in the maintenance and metabolism that are required to maintain health. Perturbations in many of these symptoms occur in dogs and cats and veterinarians are often required to diagnose and treat these conditions that may last throughout the lifetime of a pet.

Cardiac diseases occur frequently in small animal patients. It is often necessary to anesthetize these animals for routine procedures (dental prophylaxis, OVH, neuter), emergency procedures (GDV, fracture repair) or for the cardiac condition itself (PDA correction, balloon valvuloplasty, pacemaker implantation).

Anesthetized patients should be continuously monitored. To augment the anesthetist's senses, electronic monitors have been developed to allow for a more precise picture of a patient's status.

Veterinary patients can present for a variety of diseases that impact the neurological system. These patients can require anesthesia for stabilization, diagnostic procedures, or surgical correction of these diseases.
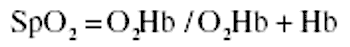
Over the past two decades, technologies have developed to allow for rapid and continuous determination of many physiologic parameters in anesthetized and critical care patients. Two of the most important modalities are pulse oximetry and capnometry.

There is no such thing as completely safe anesthesia. Anesthesia complications can occur that can compromise a patient's health and even result in death. Many anesthetic complications and accidents can be minimized or avoided with proper knowledge and avoidance techniques and vigilant patient preparation and monitoring.

Pain management in small animal medicine is one of the fastest growing areas of revenue. Veterinarians should be knowledgeable about pain management because not only is it good medicine, clients think we already know about it and are doing something for their pets, our technicians are talking to each other about pain and our treatment of it.

Although age itself is not a disease, advanced age can be a predictor for increased risk of certain disease conditions. Additionally, as our patients age, normal changes occur in their physiology that can change their responses to anesthesia and analgesic medications as well as potentially put them at higher risk of peri-anesthetic complications.

Anesthesia of the pregnant dog or cat falls into two categories, anesthesia of a pregnant animal for a procedure unrelated to the pregnancy and anesthesia of a pregnant animal specifically for a problem related to the pregnancy/cesarean section. Anesthesia of a pregnant animal for procedures unrelated to the pregnancy is often not problematic unless the animal is in a compromised state.