
A comprehensive overview of tick-transmitted infectious diseases. (1 CE credit)

A comprehensive overview of tick-transmitted infectious diseases. (1 CE credit)

Brisbane, Australia -- A three-way agreement facilitated by a $300,000 grant will result in the production of a new treatment for the deadly Hendra virus at the University of Queensland in Brisbane.

In just the past 3 to 5 years, advanced diagnostic capabilities have enhanced our ability to detect infectious pathogens in the dog and have given credence to the term "emerging" infections. However, the ever-expanding list of "emerging infectious diseases", in fact, may not be emerging at all...as it appears; many of these infections have, quite likely, existed in dogs for several years. It's the emerging technology that has enabled our ability to detect these infections.

As long as we've known about, tried to diagnose, and attempted to treat feline infectious peritonitis (FIP), it still eludes us! This complex (....and getting more complex all the time) infection of kittens and adult cats is caused by a feline Coronavirus (FCoV).

Today, the list of licensed vaccines for just the dog and cat is large and diverse ...approximately 110 canine vaccines and 70 feline vaccines are available. Considerable differences among vaccines for the same antigen exist.

Closely related to Bordetella pertussis, the cause of "whooping cough" in humans, Bordetella bronchiseptica is a gram negative, aerobic coccobacillus particularly well adapted to colonize the ciliated respiratory epithelium of dogs and cats. (NOTE: it's known today that B. bronchiseptica is the progenitor of all 9 recognized Bordetellae).

Chronic bronchial disease (CBD) is a general term used to describe a complex, progressive respiratory syndrome characterized by excessive mucous secretion within airways and thickening (hyperplasia of smooth muscle and epithelium) in the bronchial tree and frequent coughing.

The feline retroviruses, FeLV and FIV, today are well recognized for their ability to cause profound immune-suppressive disease in cats throughout the world. Clearly among the most complex infections affecting the cat, a retroviral infection demands an immune response that is robust and sustained if the infected cat is to survive long-term.

There is little argument among veterinarians that feline viral upper respiratory disease is perhaps the most common respiratory disorder for which cats are presented. In multiple-cat households and animal shelters world-wide, transmissible feline upper respiratory disease (URD) represents the most prevalent clinical disease in the population of cats at risk.
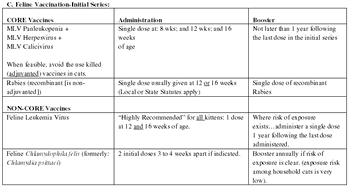
Over the last decade, publication of vaccination guidelines for the dog and cat have represented an effort on behalf of scientists, academicians, industry, and practicing veterinarians to develop recommendations based on the most current scientific studies available.

In 1985, the National Institutes of Health established the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) with the goal of reducing the prevalence of high blood cholesterol in the United States. The program, which is still in effect today, is aimed at increasing the general public's awareness of the fact that there is an undisputed risk of coronary heart disease associated with elevated cholesterol levels, particularly low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol.

Roseland, N.J. -- The United States Department of Agriculture granted full license today to the first canine influenza vaccine, Nobivac® Canine Flu H3N8.

National Report - A "highly virulent" strains of the fungus Cryptococcus gattii is spreading in the Pacific Northwest and infectin gboth humans and animals.

Microbiologists identify and deactivate trigger to EHEC colonization in grain-fed cattle.



Taking the BizQuiz? This is the answer to question 5 of "Can you battle job burnout?"

Portland, Ore. -- A "highly virulent" strain of the fungus Cryptococcus gattii is spreading in the Pacific Northwest and infecting both humans and animals, according to a recent study. But Oregon's public health veterinarian and one of the study's co-authors say media reports have exaggerated the threat of the rare fungal infection.

Streptococci species are being recognized now as potential veterinary pathogens.
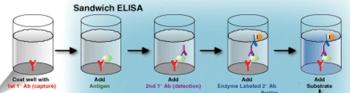
Simplified, there are two arms of the immune response: the innate immune response and the adaptive immune response. Realistically, these two arms are intimately entwined and difficult to separate.

Between 6 and 8 million dogs and cats are admitted to animal shelters each year in the United States. Often the animals admitted are unvaccinated, undernourished, stressed, and carrying one or more diseases.

Since 1990, more than 22 Bartonella species have been described, of which at least half have been implicated or confirmed as animal or human pathogens.

Las Vegas - New data suggests that nearly half of the states in this country reported 500-plus Lyme positive dogs between 2001 and July 2009.
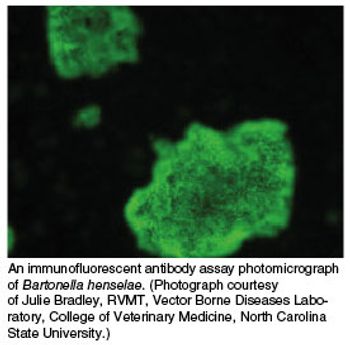
More and more, veterinarians are being asked to answer questions regarding potentially zoonotic diseases. When it comes to bartonellosis, the answers can be particularly tough to formulate because of the disease?s frequently vague or absent clinical signs and the difficulty in identifying and controlling the infection.