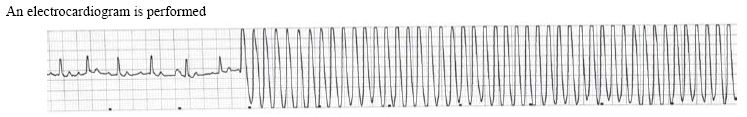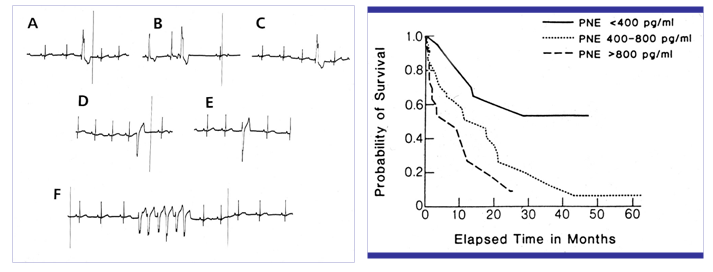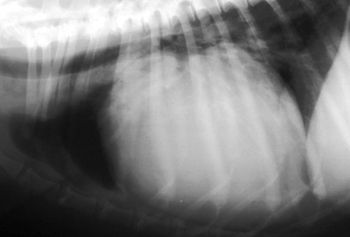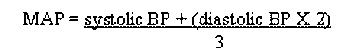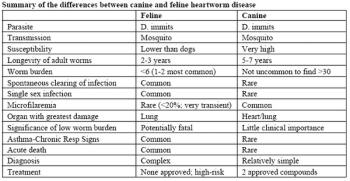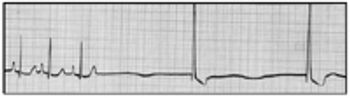
In cytology, cells that are properly smeared and stained can be described as "fried eggs" because of the similarity in the appearance of the nucleus and cytoplasm to the egg yolk and white. If the preparation is too thick, or is improperly stained, the cell outline may be seen, but intracellular detail will not be visible.