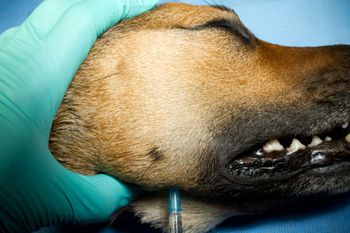
Get answers to your most commonly asked questions about two essential components of dental care in veterinary patients.

Get answers to your most commonly asked questions about two essential components of dental care in veterinary patients.

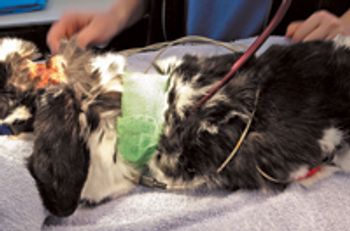
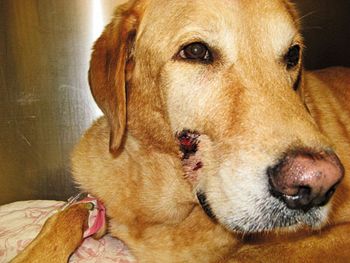
Skin graft techniques used in human medicine utilized in veterinary treatment of Northstar's wounds.

Skin graft techniques used in human medicine utilized for Northstar?s wounds.

An intensive area of study, laminitis still confounds veterinary researchers looking to advance our knowledge of disease origin, prevention and treatment. But some promising new research projects are looking to make great strides toward better understanding.

My dog was wasting away. When all else failed, I had to try something new.
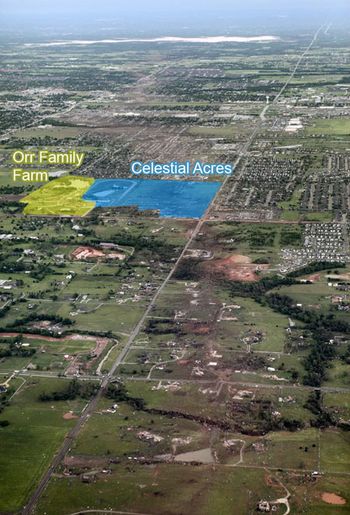
Tornado carved a path through the equine training facility causing mass horse casualties.
A way to make sure your stethoscope stays out of the way during anesthetic monitoring.

State veterinarian manages effort, including disposal of mass equine casualties.

Veterinarian, investigators seize 19 horses found to be sore in Larry Wheelon's barn.
Substance abuse can easily run rampant in a veterinary clinic environment. Make sure you-and your practice-are protected.

HR 1528 would exempt veterinarians from DEA restrictions on transporting controlled substances.
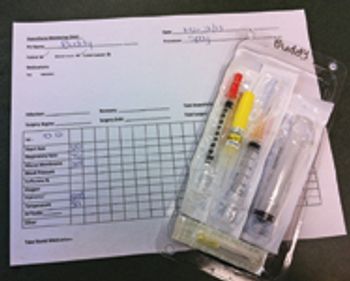
A handy way to individualize anesthetic prep materials for each patient.

Controlling chronic pain in cats is certainly a complex issue. Dr. Sheilah Robertson, feline pain expert, explains why.

Keen observation will provide veterinarians clues to diagnose pain in cats.

Recent findings point to new ways to monitor fluid therapy perioperatively and to gear fluid therapy protocols to each individual animal.
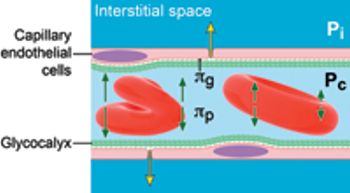
Every anesthetic and surgical circumstance warrants its own unique fluid requirements.

Vital information to help you decided which IV fluid is best in each patient.
Why you and your team need to adopt a new term-COHAT-to encompass all the facets of regular dental care.

Try these sleeved blankets for pets to keep your postop patients warm.
![photo[5]-799546-1384155729450.jpg](https://cdn.sanity.io/images/0vv8moc6/dvm360/daca0557ef671bb2aa6e8adc78734b59f6f3682b-450x613.jpg?w=350&fit=crop&auto=format)
No suspect yet in search for dog's attacker.

Peter Rule, DVM, says allegations are false, blames disgruntled former employees.
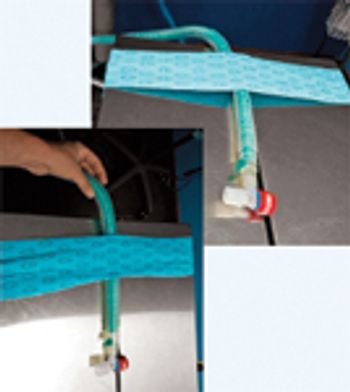
A solution for ensuring that rebreathing tubes don't dislodge endotracheal tubes during anesthesia.

Keep breathing bags accessible during anesthesia with this reader tip.

The AAHA Anesthesia Guidelines for Dogs and Cats provide recommendations for evaluating and monitoring patients from the preanesthetic period through recovery, selecting premedication and anesthetic induction and maintenance agents, and using anesthetic equipment and monitors. Take this ClinQuiz and learn how individualized anesthetic plans can help you successfully manage each patient you anesthetize.

How I kept my crazy clients from glimpsing what they must not, under any circumstances see.