
Busting the top veterinary pharmacology myths.

It is not uncommon for veterinarians working with companion animals to run into suspected intoxications where the actual toxicant cannot be identified.

An enormous amount of information can be obtained from an abdominal radiograph, especially in emergency/critical care situations.

It has been my experience in an academic environment that mycotoxicoses are generally thought to be exclusively a large animal problem.

Opioids are commonly used in veterinary medicine for their analgesic, sedative, and anti-diarrhea properties.

It is not uncommon for veterinarians working with companion animals to run into suspected intoxications where the actual toxicant cannot be identified.

Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) provides insight on the internal exposure of drug available to reach the site of action.
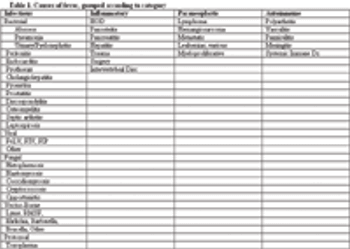
Fever of Unknown Origin (FUO) is defined in human medicine as an illness of more than 3 weeks duration, with a fever 1.5 ?F above normal body temperature on multiple occasions, the cause of which remains uncertain after 1 week of in-hospital investigation.

Gastrointestinal (GI) prokinetic drugs stimulate smooth muscle contractions to enhance gastric emptying and transit of the small and large intestines.

It is not uncommon for veterinarians working with companion animals to run into suspected intoxications.
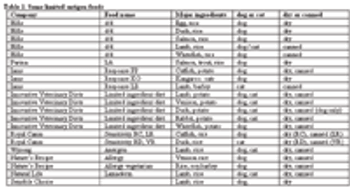
Dietary management is a vital component of successful treatment of many Gastrointestinal (GI) diseases.

A guideline to managining common household toxins.
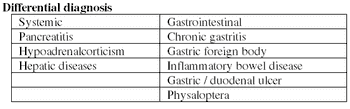
Chronic vomiting (intermittently or continuously for at least 7 days) in dogs and cats is a common and frustrating problem for clients and veterinarians.

Drug-induced diseases are commonly encountered and described as adverse drug reactions i.e. an undesirable effect of drug treatment.

The heifer selection program is a vital aspect of a commercial cow-calf operation.

Practical management of severe wounds and open fractures begins with initial assessment and management.

Constipation is a frequent complaint middle aged to older cats. In some cases the disease becomes refractory enough to treatment that either subtotal colectomy or euthanasia have to be considered.

In recent years, vaccination protocols have undergone a number of changes, such as which vaccines to give, when, and how often.

The principles of management of patients with severe lung disease and injury are summarized and the cases depicting the use if these management techniques are presented.

Several insidious diseases cause significant economic loss to sheep and goat producers through decreased longevity, growth rate, milk production and animal sales, and they are often purchased through inapparent carriers.

The object of this review is to convey new scientific information and resultant practical techniques applicable to the care of the severely injured patient.

Guidelines for immunosuppressive therapy

Both USDA and FDA classify all sheep and goats as food animals regardless of the reason that the producer chooses to maintain them.

Vaccines are such a routine part of everyday veterinary practice that we often forget about potential reactions and complications until they occur.

There are a number of causes of decreased platelets in dogs and cats, but whenever platelet counts fall acutely an immune-mediated disorder should be suspected.

A guide to proper semen collection and shipment.

Practitioners may choose to vaccinate with most or all of the vaccines available, with the belief that prevention is better than treating the disease.

The testis can be affected with several types of tumors.

As with canine vaccines, feline products are now categorized as core, noncore, and not generally recommended.

In some ways, diagnosing disease in cats is more difficult than in dogs.