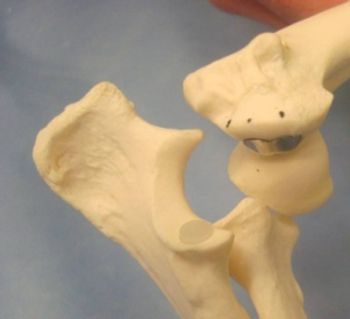
Hip dysplasia is an abnormal development of the coxofemoral joint.
College of Veterinary Medicine Texas A&M University College Station, Texas

Hip dysplasia is an abnormal development of the coxofemoral joint.
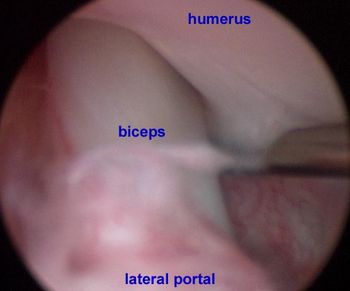
Osteochondritis dissecans OCD is a manifestation of osteochondrosis in which a flap of cartilage is lifted from the articular surface.
Dogs with strain of the supraspinatus tendon present with a chronic foreleg lameness, some dogs will exhibit periods of non weight bearing lameness.

For any fracture patient, the decision as to which stabilization system to apply is made by assessing the mechanical, biologic, and clinical factors that influence outcome. There are two mechanisms by which a fracture can be stabilized: (1) internal or external fixation and (2) formation of a biobuttress (biological buttress, callus).

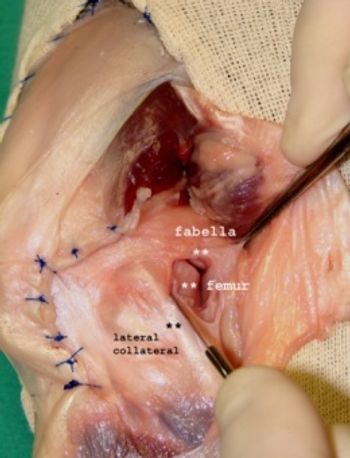
Hip dysplasia is an abnormal development of the coxofemoral joint. The syndrome is characterized by subluxation or complete luxation of the femoral head in the younger patient while in the older patient mild to severe degenerative joint disease is present.

Management of articular cartilage lesions is based on the concept that providing blood with mesenchymal stem cell precursors access to the lesion encourages healing by formation of fibrocartilage. Several marrow stimulating techniques have been described to achieve this.

Forelimb lameness can often be a diagnostic challenge in sporting breeds and active family pets. Commonly the owner reports the presence of a long standing lameness which has not resolved with the application conservative treatment modalities such as physical therapy (rest, therapeutic ultrasound, aquatic therapy), NSAIDs, nutraceuticals, and other traditional modalities.

Surgical intervention for clinical problems arising from a traumatic episode (fracture, ligament sprain) or congenital abnormality (elbow dysplasia, hip dysplasia) is a common procedure in veterinary practice.

History may be of help but be careful not to over interpret the description provided by the owner as it may be misleading. Often the owner may observe lameness in one limb when the condition is bilateral. With the latter, the dog will be lame in the limb that is more painful; however the lameness may shift from one side to the other.
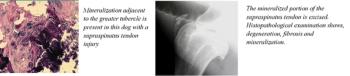
Musculotendinous injuries occur infrequently in dogs and cats, but the consequence of such an event can lead to marked dysfunction due to disruption of the muscle-tendon unit (MTU). The MTU is composed of the muscle origin, muscle belly, tendon and tendon insertion.

Published: August 1st 2011 | Updated:

Published: August 1st 2011 | Updated:

Published: August 1st 2011 | Updated:

Published: August 1st 2011 | Updated:

Published: August 1st 2011 | Updated:

Published: August 1st 2011 | Updated: