K. Gary Magdesian, DVM, DACVIM, DACVECC, DACVCP, CVA
Articles by K. Gary Magdesian, DVM, DACVIM, DACVECC, DACVCP, CVA

Clostridium difficile is the most common cause of antibiotic-associated diarrhea and pseudomembranous colitis in humans and horses. Risk factors in man include systemic antimicrobial use, gastrointestinal surgery, proton pump inhibitors (like omeprazole), chemotherapy, increasing age, and lack of immune competence.

In general, sufficient fluids have been given when the horse/foal begins to pass urine.

Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) was first described in the human health care setting in the 1960's. Infections were first described in otherwise healthy people in the 1980's. Disease severity in humans ranges from asymptomatic colonization of the upper respiratory tract and skin, to clinical disease with varying severity.

For diseases, there is a 'disease allele' (or gene mutation) and a 'normal allele' present in the population.

In evaluating a foal with established pneumonia, how can you differentiate between R. equi pneumonia from those caused by other bacteria, while waiting culture results?
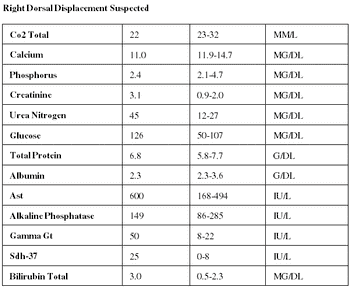
Causes of acute renal failure: 1. Hemodynamic causes; 2. Toxic causes; 3. Inflammatory causes.

Neurological disease represents 0.3% (affecting between 0.2 and 0.5% of horses depending on age) of all health problems identified by owners in the latest 2005 Equine National Animal Health and Monitoring Study (NAHMS).14 Likely this is much higher given losses in young horses due to non-infectious neurological causes, in all ages of horses from underreporting of encephalitis, and misdiagnoses of these diseases as lameness and trauma.



