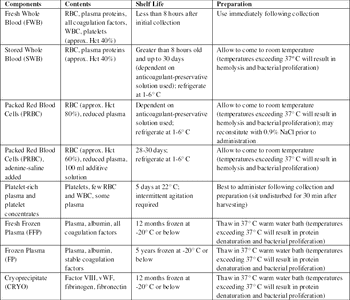
A safe and adequate supply of blood components for transfusion is indispensable.

A safe and adequate supply of blood components for transfusion is indispensable.
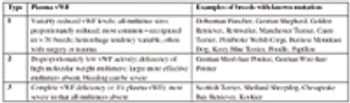
Accurate diagnosis and treatment of the bleeding patient requires a basic understanding of the pathophysiology of hemostasis.
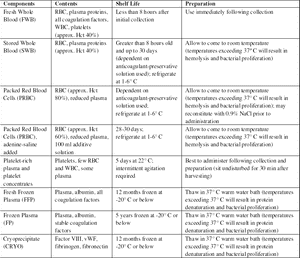
Whole blood can be stored or processed into one or more of the following components: red blood cells, platelets, plasma, and cryoprecipitate.

Bleeding animals often present to the emergency room in advanced stages of disease, on the verge of cardiovascular collapse, and in need of immediate therapeutic intervention.

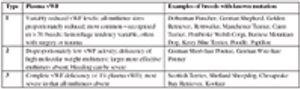
Abnormal bleeding or bruising is frequently encountered in veterinary clinical practice.
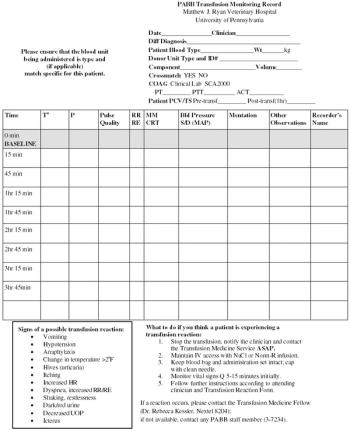
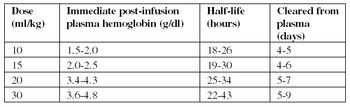
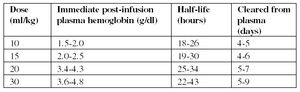
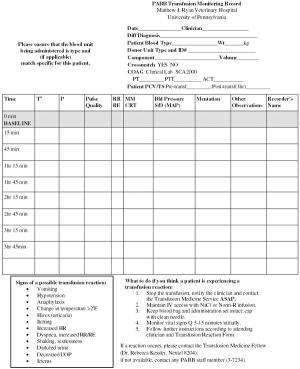
Animals should be carefully monitored for any adverse reactions during and for several weeks following transfusion.
Published: April 1st 2009 | Updated:
Published: April 1st 2009 | Updated:
Published: April 1st 2009 | Updated:

Published: April 1st 2009 | Updated:

Published: April 1st 2009 | Updated:
Published: April 1st 2009 | Updated: