Matthew P. Gerard, DVM, BVSc, PhD, DACVS
Articles by Matthew P. Gerard, DVM, BVSc, PhD, DACVS

This paper will focus on the normal anatomy of the upper airway and manipulations of the endoscope to allow a thorough examination of the region in question. Adequate restraint of the horse allows for a controlled and complete endoscopic examination. This is not always achievable. When dynamic functional collapse of the upper airway is suspected from the horse's presenting history ideally the resting endoscopic examination is performed without use of sedation. Sedatives may alter nasopharyngeal and laryngeal movements and consequently affect the assessment of the airway.

Horses with evidence of epistaxis can be challenging to diagnose and manage. The volume of visible blood can range from a trace of serosanguinous discharge that is suggestive of a past episode of bleeding, to high volume fresh blood flow from both nares.
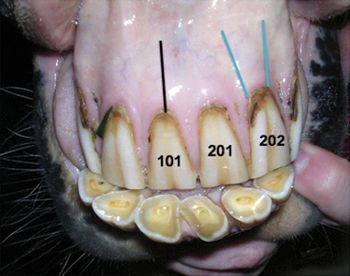
The principles of extracting teeth are very similar, regardless of the tooth one is attempting to remove. Private practitioners are familiar with the routine extraction of wolf teeth (modified Triadan #05). With an investment in instruments, an understanding of techniques, the use of regional head anesthesia, and systemic sedatives, more extractions can be performed with time and patience.
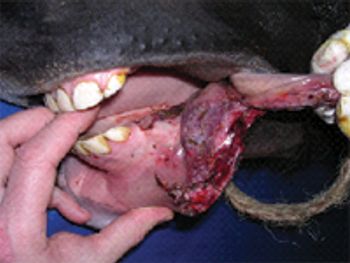
The soft tissues of the oral cavity are susceptible to traumatic injuries by bits or other oral tack, sharp external objects, blows to the head, injury during recovery from general anesthesia, and iatrogenic damage during intraoral procedures-for example, administration of oral medications, dental extraction, or transoral epiglottic entrapment release.
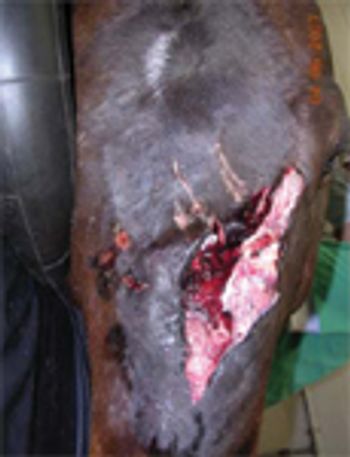
The horse is prone to traumatic injury of its head. Environmental conditions, a heightened flight response, and equipment and tack used for the horse all contribute to injury occurrence.
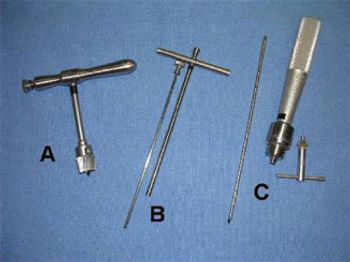
The equine paranasal sinuses (PNS) are an intricate area of the head. There are 6 paired sinuses (frontal, maxillary, dorsal conchal, ventral conchal, middle conchal, and sphenopalatine) and all of these spaces communicate with each other and the nasal passage either directly or indirectly.
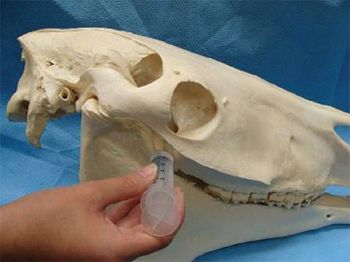
Regional or local anesthesia of the equine head greatly facilitates performing standing procedures that are anticipated to elicit pain in the patient. With effective local anesthesia, less systemic sedatives may be required for standing surgeries (e.g. dental extractions, laceration repairs, incisor avulsion repairs), patients under general anesthesia can be run at a lighter plane of anesthesia, and postoperative pain may be lessened if effective preemptive analgesia is in place.












