- dvm360 September 2021
- Volume 52
Tricky toes: Considerations regarding canine digit amputation
Insights and tips to ensure success for this common surgical procedure.
Digit amputation may be indicated due to neoplasia, osteomyelitis, or trauma. In many of these scenarios, amputation of the affected digit(s) can be the simplest, most effective, and most cost-efficient method to return the patient to health. Although this procedure is routinely performed, there are aspects of this straightforward surgery that can be more complicated.
What if I need to remove digit 3 or 4?
Due to digits 3 and 4 being responsible for more weight bearing, there has long been concern that amputation of either of these digits may result in long-term lameness or an unacceptable outcome. A retrospective study concluded that dogs that underwent amputation of digit 3, 4, or both, did not seem to have a worse outcome than dogs that underwent amputation of other digits.1 Previous reports describing increased incidence of persistent lameness after amputation of digits 3 and 4 were often associated with resection of the digit through the mid to distal region of P1 or P2. Removal of the bone remnant was found to resolve lameness in the 3 reported cases.2 It has become many practitioners’ preference to amputate via disarticulation at the level of the metacarpo/metatarsophalangeal joint. Amputation at other sites is still acceptable, but a more proximal metacarpo/metatarsophalangeal amputation may be warranted for digits 3 and 4.
What if I need to amputate more than 1 digit?
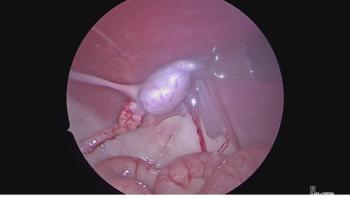
Amputation of more than 1 digit (partial foot amputation) can result in good patient outcomes (Figure 1). In a small series of 11 dogs treated with partial foot amputation, lameness resolved in 8 dogs after a median of 37 days.3 The mild lameness that persisted in the remaining 3 dogs did not seem to impact their quality of life, and all owners were satisfied with the outcome. Another study found similar results, with both dogs in this study returning to full function after partial foot amputation.1 In fact, they also found it is possible to remove all digits and still have a functional and pain-free foot if the metacarpal/tarsal pad is preserved.
What if I don’t have enough skin to close a paw defect?
Another complication associated with surgery on the foot is a shortage of skin needed to close a defect on the paw. This is common in cases of large mass removals or shearing injuries. In these scenarios, a technique termed the phalangeal fillet is used to transpose skin from a sacrificed digit over the defect in the paw (Figure 2). Although a relatively more complex procedure, this unique flap allows for closure of defects that would otherwise be impossible.
What about routine complications?
Short-term lameness is to be expected immediately following surgery for uncomplicated digit amputation; however, other complications are common as well. One study found that nearly 40% of dogs had short-term complications, other than lameness, following digit amputation.1 These complications included dehiscence with and without infection, discharge from the wound, and delayed healing attributed to licking by the dog.
Owners should be made aware of the potential for short-term complications; however, long-term outcomes are typically excellent. Minimization of complications may be achieved with meticulous surgical technique (in particular, tension-free closure and precise apposition) and owner compliance with e-collar use or bandage management. Applying a light, soft, and padded bandage for 1 to 2 weeks postoperatively is common and may help protect the incision from environmental contaminants, licking, and splaying of the digits during early weight bearing. Discontinuation of bandaging may be necessary if pododermatitis or bandage management becomes an issue.
Conclusion
Although short-term complications are relatively common after digit amputation, this surgery is typically well tolerated by dogs with good long-term outcomes. Nonetheless, clients should be informed of potential complications to ensure a positive experience for both the client and patient.
Kassidy Burgess, BS, is a fourth-year veterinary student at Midwestern University in Arizona. She has a strong passion for small animal surgery and hopes to complete a surgical residency in the future. In her free time, Kassidy loves road trips and exploring the great outdoors.
Stephanie Shaver, DVM, DACVS-SA, is an ACVS board-certified veterinary surgeon and assistant professor of small animal surgery at Midwestern University in Arizona. She enjoys hiking, travel, friends, family, and teaching veterinary students.
References
- Kaufman KL, Mann FA. Short- and long-term outcomes after digit amputation in dogs: 33 cases (1999-2011). J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2013;242(9):1249-1254. doi:10.2460/javma.242.9.1249
- Muir P, Pead MJ. Chronic lameness after digit amputation in three dogs. Vet Rec. 1998;143(16):449-450. doi:10.1136/vr.143.16.449
- Liptak JM, Dernell WS, Rizzo SA, Withrow SJ. Partial foot amputation in 11 dogs. J Am Anim Hosp Assoc. 2005;41(1):47-55. doi:10.5326/0410047
Articles in this issue
over 4 years ago
How would Walt Disney run a veterinary practice?over 4 years ago
Tips and tricks for performing an orthopedic examover 4 years ago
Take your team H.I.G.H.E.R.over 4 years ago
Veterinary receptionist program simplifies CSR trainingover 4 years ago
Nutritional management of urolithiasis in dogs and catsover 4 years ago
Studied cats show little interest in contrafreeloadingover 4 years ago
Designing an award-winning animal hospitalover 4 years ago
The COVID-19 pet adoption boom: Did it really happen?Newsletter
From exam room tips to practice management insights, get trusted veterinary news delivered straight to your inbox—subscribe to dvm360.