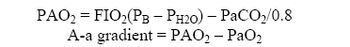Vicki L. Campbell, DVM, DACVA, DACVECC
Articles by Vicki L. Campbell, DVM, DACVA, DACVECC
In order to understand and approach hypotensive patients, one must first understand blood pressure. Although not a true measure of perfusion, blood pressure is one of the most non-invasive means the veterinary field has of measuring whether or not the tissues are getting enough blood and ultimately enough oxygen.

According to Webster's dictionary, inflammation is defined as "a local response to cellular injury that is marked by capillary dilatation, leukocytic infiltration, redness, heat, and pain and that serves as a mechanism initiating the elimination of noxious agents and of damaged tissue."

The triage examination is the initial and brief examination that occurs in the first few minutes after a patient presents to the emergency room. The triage examination is crucial to assessing a patient and determining if life-threatening problems are present. Point-of-care testing is a term used to refer to immediate testing in an emergency room.

In general, shock is defined as abnormal oxygen delivery and/or oxygen utilization at the tissue level. Oxygen delivery to the tissues is one of the primary functions of the cardiopulmonary system and of primary importance to the patient manifesting signs of circulatory failure.
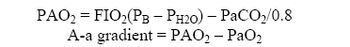
The decision to mechanically ventilate or dialyze a dog or cat is a difficult one. It is challenging from an expertise, staffing, emotional, ethical, and monetary perspective.

The treatment of head trauma is a controversial topic in veterinary medicine. Unfortunately, there does not appear to be a generalized consensus as to the approach to treating head trauma.