
In recent decades, it has become well known that animals use plants to self-medicate.

In recent decades, it has become well known that animals use plants to self-medicate.
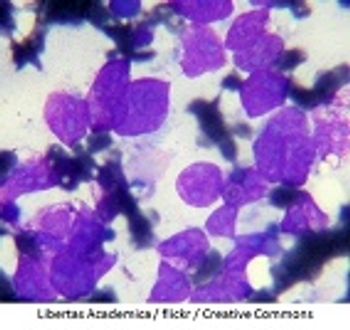
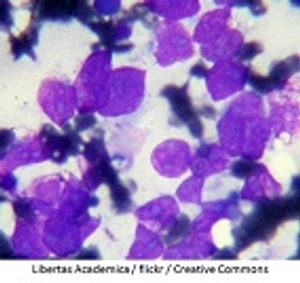
In a review article published in Frontiers in Veterinary Science, Luca Aresu, DVM, PhD, from the University of Padova, Legnaro, Italy, reviews some of the most recent advances and the characteristics of canine DLBCL.

A review article explores possible reasons that might explain why cats and dogs are not susceptible to all of the same types of diseases.
Environmental conditions as well as interactions between different parasites co-infecting wild birds may be important in determining whether the birds will develop a malaria infection.

Many domestic and wild animals, especially rodents, serve as chronic, asymptomatic carriers of Leptospira, and excrete the bacteria in their urine.

For the first time, a recent study has captured African monkeys eating bats—a finding that raises concern about the spread of zoonotic diseases such as Ebola.

A recent study has found that low rectal temperature at the time of hospital admission is a significant predictor of death in pet rabbits.

Adding controlled physical exercise to a weight loss program for pet dogs helps preserve muscle mass more effectively than calorie restriction alone.

Chimpanzees that socialize more have a greater diversity of bacteria in their gut.

Recent advances have led to immunotherapy that is not only changing the standard of care for human cancer patients, but also moving to the forefront of cancer treatment options for veterinary patients.
Published: September 16th 2016 | Updated:

Published: October 3rd 2016 | Updated:
Published: October 4th 2016 | Updated:

Published: October 11th 2016 | Updated:

Published: February 13th 2016 | Updated:

Published: February 13th 2016 | Updated: