Maureen Long, DVM, PhD, DACVIM
Articles by Maureen Long, DVM, PhD, DACVIM
Maintenance of excellent health and biosecurity standards at the level of the farm is the MOST effective way of maintaining an outbreak-free industry. All disease outbreaks have an index case and all index cases have a point of origin. Because horses are usually maintained at a "home" farm, then the origin of any outbreak should be traced back to the farm level.
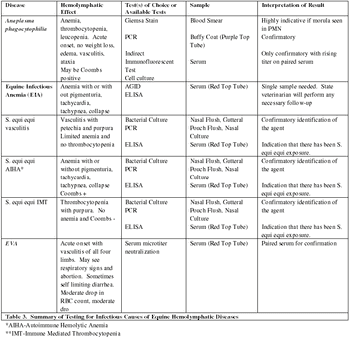
Infectious and non-infectious hemolymphatic diseases generally present with the same clinical symptoms due to cardiovascular insult, lack of tissue oxygenation and possible impending cardiovascular collapse.

The main advantage of genomic strategies for testing is that a live organism is not necessarily needed for diagnosis. While the fact that diagnosis based on molecular techniques does not require live organism, DNA and RNA are subject to the same microbiological, biochemical and physical factors as live organism for degradation.

Staphylococcus aureus is an important human pathogen and is a significant cause of hospital acquired (nosocomial) infection of surgical wounds and infections associated with indwelling medical devices. Staphylococcus aureus can colonize the skin and nares of humans which facilitate its transmission, particularly in the healthcare setting.
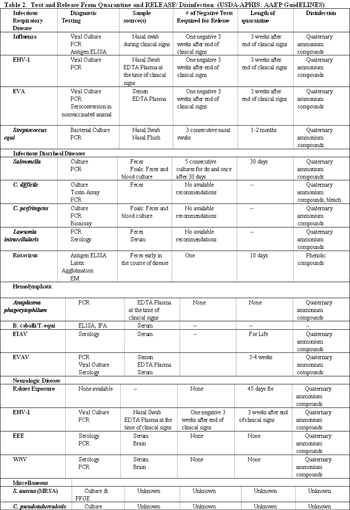
Salmonella enteriticus, Neorickettsia risticii (Potomac Horse Fever), Clostridium difficile and Clostridium perfringens are most commonly associated with infectious diarrhea in adults. Foals can have a variety of agents including viral causes and bacterial such as Lawsonia intracellularis.

Neurological disease represents 0.3% (affecting between 0.2 and 0.5% of horses depending on age) of all health problems identified by owners in the latest 2005 Equine National Animal Health and Monitoring Study (NAHMS).14 Likely this is much higher given losses in young horses due to non-infectious neurological causes, in all ages of horses from underreporting of encephalitis, and misdiagnoses of these diseases as lameness and trauma.
The clinical signs of VEE are similar to both EEE and VEE with a large variation in mortality ranging from 40-90% depending on the outbreak. In addition to subclinical and overt CNS clinical signs, diarrhea has been observed in VEE horses. Florida, Texas, and Louisiana are the three states ecologically at risk but recent activity in Panama could result in a transported case by air travel.
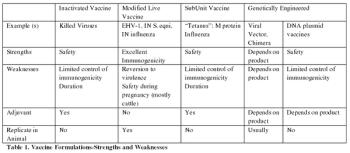
The deliberate induction of active immunity to an agent by exposure to the agent or to non-replicating components, with the intent of inducing protective immunity to challenge with a virulent infectious agent, is termed "vaccination". Actively acquired immunity is that provided by an antigen specific response of the challenged host's own immune system in response to materials recognized as non-self.

Veterinarians are the first line of defense against infectious disease outbreaks. Current problem and case based equine medicine likely does not prepare new graduates in outbreak control. Control of an infectious disease is based on correct application of the principles of population biology and transmission dynamics of a particular infectious organism, basic microbiology, and basic epidemiology.
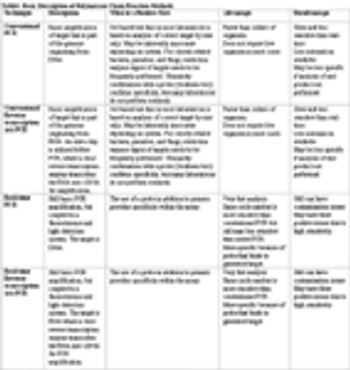
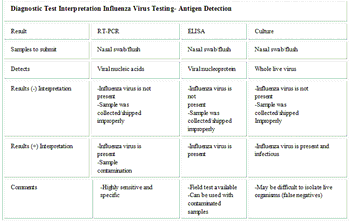
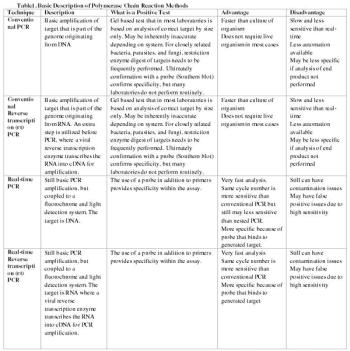
Several previous presentations at the ACVIM and at other veterinary meetings have discussed PCR, and a recent paper indicates that a basic understanding of the different PCR test formats is needed for continuing education of practitioners and diplomates. While it is not necessary for the practitioner to be a molecular biologist, this table provides a short review of the definitions of molecular testing.
Staphylococcus aureus is an important human pathogen and is a significant cause of hospital acquired (nosocomial) infection of surgical wounds and infections associated with indwelling medical devices. Staphylococcus aureus can colonize the skin and nares of humans which facilitate its transmission, particularly in the healthcare setting.
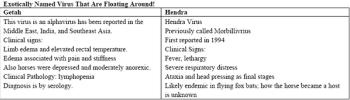
The clinical signs of VEE are similar to both EEE and VEE with a large variation in mortality ranging from 40-90% depending on the outbreak. In addition to subclinical and overt CNS clinical signs, diarrhea has been observed in VEE horses. Florida, Texas, and Louisiana are the three states ecologically at risk but recent activity in Panama could result in a transported case by air travel.
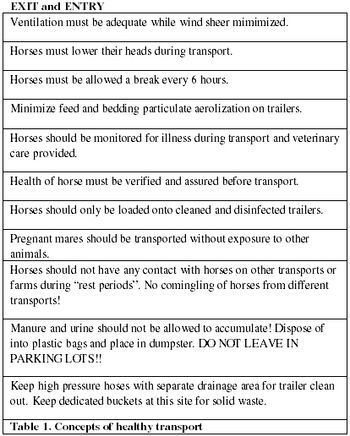
Maintenance of excellent health and biosecurity standards at the level of the farm is the MOST effective way of maintaining an outbreak-free industry. All disease outbreaks have an index case and all index cases have a point of origin. Because horses are usually maintained at a 'home" farm, then the origin of any outbreak should be traced back to the farm level.

Neurological disease represents 0.3% (affecting between 0.2 and 0.5% of horses depending on age) of all health problems identified by owners in the latest 2005 Equine National Animal Health and Monitoring Study (NAHMS).14 Likely this is much higher given losses in young horses due to non-infectious neurological causes, in all ages of horses from underreporting of encephalitis, and misdiagnoses of these diseases as lameness and trauma.
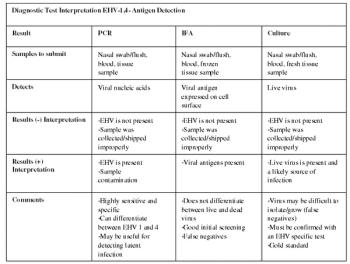
Salmonella enteriticus, Neorickettsia risticii (Potomac Horse Fever), Clostridium difficile and Clostridium perfringens are most commonly associated with infectious diarrhea in adults. Foals can have a variety of agents including viral causes and bacterial such as Lawsonia intracellularis.
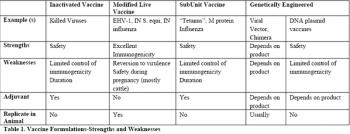
The deliberate induction of active immunity to an agent by exposure to the agent or to non-replicating components, with the intent of inducing protective immunity to challenge with a virulent infectious agent, is termed "vaccination". Actively acquired immunity is that provided by an antigen specific response of the challenged host's own immune system in response to materials recognized as non-self.
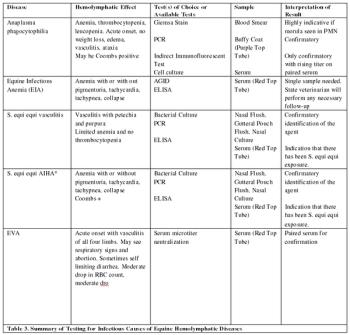
Infectious and non-infectious hemolymphatic diseases generally present with the same clinical symptoms due to cardiovascular insult, lack of tissue oxygenation and possible impending cardiovascular collapse. Frequently, bacterial sepsis is hard to differentiate from viral diseases.

Staphylococcus aureus is an important human pathogen and is a significant cause of hospital acquired (nosocomial) infection of surgical wounds and infections associated with indwelling medical devices. Staphylococcus aureus can colonize the skin and nares of humans which facilitate its transmission, particularly in the healthcare setting.























